GRP94 is essential for mesoderm induction and muscle development because it regulates insulin-like growth factor secretion
- PMID: 17634284
- PMCID: PMC1995707
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-03-0275
GRP94 is essential for mesoderm induction and muscle development because it regulates insulin-like growth factor secretion
Abstract
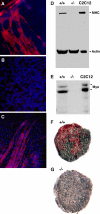
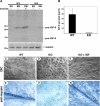
Because only few of its client proteins are known, the physiological roles of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone glucose-regulated protein 94 (GRP94) are poorly understood. Using targeted disruption of the murine GRP94 gene, we show that it has essential functions in embryonic development. grp94-/- embryos die on day 7 of gestation, fail to develop mesoderm, primitive streak, or proamniotic cavity. grp94-/- ES cells grow in culture and are capable of differentiation into cells representing all three germ layers. However, these cells do not differentiate into cardiac, smooth, or skeletal muscle. Differentiation cultures of mutant ES cells are deficient in secretion of insulin-like growth factor II and their defect can be complemented with exogenous insulin-like growth factors I or II. The data identify insulin-like growth factor II as one developmentally important protein whose production depends on the activity of GRP94.
Figures

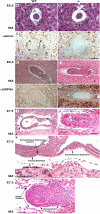
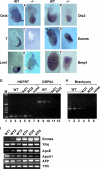
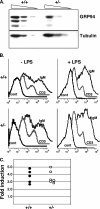
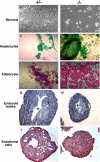
References
-
- Anderson K. V., Bokla L., Nusslein-Volhard C. Establishment of dorsal-ventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo: the induction of polarity by the Toll gene product. Cell. 1985;42:791–798. - PubMed
-
- Bain G., Kitchens D., Yao M., Huettner J. E., Gottlieb D. I. Embryonic stem cells express neuronal properties in vitro. Dev. Biol. 1995;168:342–357. - PubMed
-
- Baker J., Liu J. P., Robertson E. J., Efstratiadis A. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell. 1993;75:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Barnes J. A., Smoak I. W. Immunolocalization and heart levels of GRP94 in the mouse during post-implantation development. Anat. Embryol. 1997;196:335–341. - PubMed
-
- Barnes J. D., Crosby J. L., Jones C. M., Wright C. V., Hogan B. L. Embryonic expression of Lim-1, the mouse homolog of Xenopus Xlim-1, suggests a role in lateral mesoderm differentiation and neurogenesis. Dev. Biol. 1994;161:168–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

