Serotype IX, a Proposed New Streptococcus agalactiae Serotype
- PMID: 17634306
- PMCID: PMC2045254
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00117-07
Serotype IX, a Proposed New Streptococcus agalactiae Serotype
Abstract
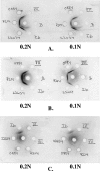
We identified three isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae (group B streptococcus [GBS]), of human origin, which failed to react with antisera against any of the nine known GBS serotypes. Polyclonal rabbit antisera raised against these isolates and standard GBS typing sera were used in capillary precipitation and Ouchterlony tests to compare the strains with known GBS serotype reference strains. All three previously nontypeable isolates reacted with all three new antisera, producing lines of identity in the Ouchterlony test. Weak cross-reactions with antisera against several GBS serotypes were observed but were removed by absorption with corresponding antigens. The new antisera were used to test 227 GBS isolates that had been nontypeable or difficult to type using standard antisera. Of these, five reacted with the new antisera. These results suggested that all eight isolates belong to the previously unrecognized GBS serotype. They were tested by Western blotting for the Calpha and Cbeta proteins and by PCR to identify molecular serotypes and surface protein antigen genes. Two segments of the cps gene cluster (3' end of cpsE-cpsF and 5' end of cpsG, approximately 700 bp; 3' end of cpsH and 5' end of cpsM, approximately 560 bp) were sequenced. All eight isolates expressed Calpha, and seven expressing the Cbeta protein and the corresponding genes, bca and bac, respectively, were identified. They all share the same, unique partial cps sequence. These results indicate that these eight isolates represent a new S. agalactiae serotype, which we propose should be designated serotype IX.
Figures

References
-
- Benson, J. A., A. E. Flores, C. J. Baker, S. L. Hillier, and P. Ferrieri. 2002. Improved methods for typing nontypeable isolates of group B streptococci. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 292:37-42. - PubMed
-
- Bentley, S. D., D. M. Aanensen, A. Mavroidi, D. Saunders, E. Rabbinowitsch, M. Collins, K. Donohoe, D. Harris, L. Murphy, M. A. Quail, G. Samuel, I. C. Skovsted, M. S. Kaltoft, B. Barrell, P. R. Reeves, J. Parkhill, and B. G. Spratt. 2006. Genetic analysis of the capsular biosynthetic locus from all 90 pneumococcal serotypes. PLoS Genet. 2:262-269. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berner, R., A. Bender, C. Rensing, J. Forster, and M. Brandis. 1999. Low prevalence of the immunoglobulin-A-binding beta antigen of the C protein among Streptococcus agalactiae isolates causing neonatal sepsis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 18:545-550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

