Serotonin concentrations in the lumbosacral spinal cord of the adult rat following microinjection or dorsal surface application
- PMID: 17634342
- PMCID: PMC2668515
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00309.2007
Serotonin concentrations in the lumbosacral spinal cord of the adult rat following microinjection or dorsal surface application
Abstract
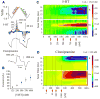
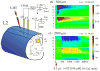
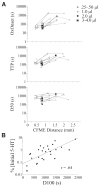
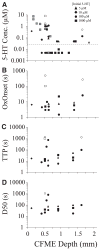
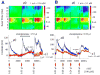
Application of neuroactive substances, including monoamines, is common in studies examining the spinal mechanisms of sensation and behavior. However, affected regions and time courses of transmitter activity are uncertain. We measured the spatial and temporal distribution of serotonin [5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)] in the lumbosacral spinal cord of halothane-anesthetized adult rats, following its intraspinal microinjection or surface application. Carbon fiber microelectrodes (CFMEs) were positioned at various locations in the spinal cord and oxidation currents corresponding to extracellular 5-HT were measured by fast cyclic voltammetry. Intraspinal microinjection of 5-HT (100 microM, 1-3 microl) produced responses that were most pronounced at CFMEs positioned <or=800 microm from the drug micropipette: 5-HT concentration was significantly higher (1.43 vs. <0.28% of initial concentration) and response latency was shorter (67.1 vs. 598.2 s) compared with more distantly positioned CFMEs. Treatment with the selective 5-HT reuptake inhibitor clomipramine only slightly affected the spread of microinjected 5-HT. Surface application over several segments led to a transient rise in concentration that was usually apparent within 30 s and was dramatically attenuated with increasing depth: 0.25% of initial concentration (1 mM) within 400 microm of the dorsal surface and <0.001% between 1,170 and 2,000 microm. This initial response to superfusion was sometimes followed by a gradual increase to a new concentration plateau. In sum, compared with bath application, microinjection can deliver about tenfold higher transmitter concentrations, but to much more restricted areas of the spinal cord.
Figures


References
-
- Antri M, Orsal D, Barthe J-Y. Locomotor recovery in the chronic spinal rat: effects of long-term treatment with a 5-HT2 agonist. Eur J Neurosci. 2002;16:467– 476. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong-James M, Millar J. High-speed cyclic voltammetry and unit recording with carbon fibre microelectrodes. In: Marsden CA, editor. Measurement of Neurotransmitter Release In Vivo. Toronto: Wiley; 1984. pp. 209–226.
-
- Barbeau H, Rossignol S. Initiation and modulation of the locomotor pattern in the adult chronic spinal cat by noradrenergic, serotonergic, and dopaminergic drugs. Brain Res. 1991;546:250–260. - PubMed
-
- Bardin L, Bardin M, Lavarenne J, Eschalier A. Effect of intrathecal serotonin on nociception in rats: influence of the pain test used. Exp Brain Res. 1997;113:81– 87. - PubMed
-
- Binns BC, Huang Y, Goettl VM, Hackshaw KV, Stephens RL. Glutamate uptake is attenuated in spinal deep dorsal and ventral horn in the rat spinal nerve ligation model. Brain Res. 2005;1041:38– 47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

