Abeta oligomer-mediated long-term potentiation impairment involves protein phosphatase 1-dependent mechanisms
- PMID: 17634359
- PMCID: PMC6672892
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0395-07.2007
Abeta oligomer-mediated long-term potentiation impairment involves protein phosphatase 1-dependent mechanisms
Abstract
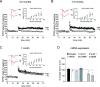
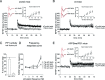
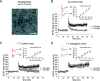
Amyloid beta (Abeta) oligomers are derived from proteolytic cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP) and can impair memory and hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) in vivo and in vitro. They are recognized as the primary neurotoxic agents in Alzheimer's disease. The mechanisms underlying such toxicity on synaptic functions are complex and not fully understood. Here, we provide the first evidence that these mechanisms involve protein phosphatase 1 (PP1). Using a novel transgenic mouse model expressing human APP with the Swedish and Arctic mutations that render Abeta more prone to form oligomers (arcAbeta mice), we show that the LTP impairment induced by Abeta oligomers can be fully reversed by PP1 inhibition in vitro. We further demonstrate that the genetic inhibition of endogenous PP1 in vivo confers resistance to Abeta oligomer-mediated toxicity and preserves LTP. Overall, these results reveal that PP1 is a key player in the mechanisms of AD pathology.
Figures
References
-
- Chen QS, Wei WZ, Shimahara T, Xie CW. Alzheimer amyloid beta-peptide inhibits the late phase of long-term potentiation through calcineurin-dependent mechanisms in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2002;77:354–371. - PubMed
-
- Demuro A, Mina E, Kayed R, Milton SC, Parker I, Glabe CG. Calcium dysregulation and membrane disruption as a ubiquitous neurotoxic mechanism of soluble amyloid oligomers. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:17294–17300. - PubMed
-
- Dodart JC, Bales KR, Gannon KS, Greene SJ, DeMattos RB, Mathis C, DeLong CA, Wu S, Wu X, Holtzman DM, Paul SM. Immunization reverses memory deficits without reducing brain Abeta burden in Alzheimer's disease model. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:452–457. - PubMed
-
- Genoux D, Haditsch U, Knobloch M, Michalon A, Storm D, Mansuy IM. Protein phosphatase 1 is a molecular constraint on learning and memory. Nature. 2002;418:970–975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
