Immunoglobulins G, M, and A against Sporothrix schenckii exoantigens in patients with sporotrichosis before and during treatment with itraconazole
- PMID: 17634504
- PMCID: PMC2043312
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00149-07
Immunoglobulins G, M, and A against Sporothrix schenckii exoantigens in patients with sporotrichosis before and during treatment with itraconazole
Abstract
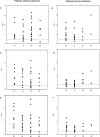
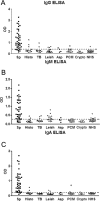
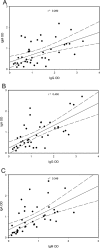
Sporotrichosis is an important subcutaneous mycosis, with an increasing worldwide incidence. However, few data are available regarding the immunological aspects of Sporothrix schenckii infection, particularly the humoral responses to the fungus. In this study we measured immunoglobulin G (IgG), IgM, and IgA in sera from 41 patients with sporotrichosis before antifungal treatment and from another 35 patients with sporotrichosis during itraconazole treatment by using a recently described S. schenckii exoantigen enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). More than 95% of patients had detectable IgA antibodies, and more than 85% had IgM and IgG antibodies before treatment. The number of patients with IgG antibodies increased to 91% during treatment. Conversely, significantly fewer samples from treated patients were positive for IgM (71%) and IgA (89%). Overall, 78% of patients had detectable levels of all isotypes tested at diagnosis, and this percentage dropped to 62.9% in patients receiving itraconazole. Testing of all three isotypes improved the sensitivity; at least two isotypes were detected in 93% of patients before and 89% after treatment. The reactivity of 94 sera from patients with other diseases and healthy individuals was also tested. Cross-reactivity occurred in 33% of the heterologous sera. Most of them were positive only in one isotype, 8.5% were positive for at least two isotypes, and only one serum (1.1%) was positive for the three isotypes. Antibodies produced during S. schenckii infection are diverse, and we demonstrate that an exoantigen ELISA for the detection of combinations of IgA, IgG, and IgM antibodies is a highly sensitive and specific diagnostic assay for sporotrichosis.
Figures

References
-
- Agudelo, S. P., S. Restrepo, and I. D. Velez. 1999. Cutaneous New World leishmaniasis-sporotrichosis coinfection: report of 3 cases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 401002-1004. - PubMed
-
- Albornoz, M. B., E. Villanueva, and E. D. Torres. 1984. Application of immunoprecipitation techniques to the diagnosis of cutaneous and extracutaneous forms of sporotrichosis. Mycopathologia 85177-183. - PubMed
-
- Almeida-Paes, R., M. A. Pimenta, C. V. Pizzini, P. C. Monteiro, J. M. Peralta, J. D. Nosanchuk, and R. M. Zancope-Oliveira. 2007. Use of mycelial-phase Sporothrix schenckii exoantigens in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of sporotrichosis by antibody detection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 14244-249. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Araujo, T., A. C. Marques, and F. Kerdel. 2001. Sporotrichosis. Int. J. Dermatol. 40737-742. - PubMed
-
- Baida, H., P. J. Biselli, M. Juvenale, G. M. Del Negro, M. J. Mendes-Giannini, A. J. Duarte, and G. Benard. 1999. Differential antibody isotype expression to the major Paracoccidioides brasiliensis antigen in juvenile and adult form paracoccidioidomycosis. Microbes Infect. 1273-278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

