EGFRvIII-targeted immunotoxin induces antitumor immunity that is inhibited in the absence of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 17634939
- PMCID: PMC2846815
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-007-0363-7
EGFRvIII-targeted immunotoxin induces antitumor immunity that is inhibited in the absence of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells
Abstract
Purpose: Immunotoxins as anti-cancer therapeutics have several potential advantages over conventional agents including a high specificity, extraordinary potency, and a lack of an identified mechanism for resistance. It has been clearly demonstrated that Pseudomonas-based immunotoxins have a direct cytotoxic effect. However, delayed and often dramatic antitumor responses seen in human studies with targeted toxins led us to hypothesize that immunologic responses may be a secondary mechanism that enhances the therapeutic efficacy of these novel drugs.
Experimental design: This hypothesis was tested in a murine system using an immunotoxin, MR1-1 [MR1-1(dsFv)-PE38KDEL], that targets a syngeneic murine homologue of the tumor-specific human epidermal growth factor mutation, EGFRvIII, expressed on a murine cell line.
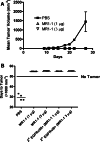
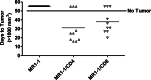
Results: Intratumoral treatment with MR1-1 eliminated EGFRvIII-expressing tumors (P < 0.0001). The antitumor activity of MR1-1 was dependent on the expression of EGFRvIII on some, but not all tumors cells, and was significantly inhibited in the absence of CD4+ (P = 0.0193) and CD8+ (P = 0.0193) T cells. MR1-1 induced EGFRvIII-specific immunity (P < 0.0005) and produced long lasting immunity against tumors expressing EGFRvIII as well as EGFRvIII-negative tumors.
Conclusions: These data suggest that immunotoxins may not be strictly dependent on direct cytotoxicity for their efficacy, but may also be potent inducers of antitumor immunity active even against cells that do not express the targeted antigen.
Figures
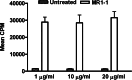
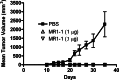

Similar articles
-
Tumor-specific immunotherapy targeting the EGFRvIII mutation in patients with malignant glioma.Semin Immunol. 2008 Oct;20(5):267-75. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2008.04.001. Epub 2008 Jun 9. Semin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18539480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytotoxic and antitumor activity of a recombinant immunotoxin composed of disulfide-stabilized anti-Tac Fv fragment and truncated Pseudomonas exotoxin.Int J Cancer. 1994 Jul 1;58(1):142-9. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910580123. Int J Cancer. 1994. PMID: 8014011
-
Improved efficacy against malignant brain tumors with EGFRwt/EGFRvIII targeting immunotoxin and checkpoint inhibitor combinations.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 May 29;7(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0614-0. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31142380 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of an immunotoxin, D2C7-(scdsFv)-PE38KDEL, targeting EGFRwt and EGFRvIII for brain tumor therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Sep 1;19(17):4717-27. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3891. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23857604 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotoxins in cancer therapy: Review and update.Int Rev Immunol. 2017 Jul 4;36(4):207-219. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2017.1284211. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Int Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28282218 Review.
Cited by
-
Production and quality control assessment of a GLP-grade immunotoxin, D2C7-(scdsFv)-PE38KDEL, for a phase I/II clinical trial.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Apr;101(7):2747-2766. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-8063-x. Epub 2016 Dec 24. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28013405 Free PMC article.
-
Convection-enhanced delivery of free gadolinium with the recombinant immunotoxin MR1-1.J Neurooncol. 2010 May;98(1):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s11060-009-0046-7. Epub 2009 Nov 7. J Neurooncol. 2010. PMID: 19898744 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Combating immunosuppression in glioma.Future Oncol. 2008 Jun;4(3):433-42. doi: 10.2217/14796694.4.3.433. Future Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18518768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-specific immunotherapy targeting the EGFRvIII mutation in patients with malignant glioma.Semin Immunol. 2008 Oct;20(5):267-75. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2008.04.001. Epub 2008 Jun 9. Semin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18539480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SS1P Immunotoxin Induces Markers of Immunogenic Cell Death and Enhances the Effect of the CTLA-4 Blockade in AE17M Mouse Mesothelioma Tumors.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Nov 14;10(11):470. doi: 10.3390/toxins10110470. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30441807 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Archer GE, et al. Regional treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor vIII-expressing neoplastic meningitis with a single-chain immunotoxin, MR-1. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:2646–2652. - PubMed
-
- Hall WA, Fodstad O. Immunotoxins and central nervous system neoplasia. J Neurosurg. 1992;76:1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

