BMP-6 exerts its osteoinductive effect through activation of IGF-I and EGF pathways
- PMID: 17634942
- PMCID: PMC2266664
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-007-0407-9
BMP-6 exerts its osteoinductive effect through activation of IGF-I and EGF pathways
Abstract
We have recently shown that human recombinant BMP-6 (rhBMP-6), given systematically, can restore bone in animal models of osteoporosis. To further elucidate the underlying mechanisms of new bone formation following systemic application of BMPs, we conducted gene expression profiling experiments using bone samples of oophrectomised mice treated with BMP-6. Gene set enrichment analysis revealed enrichment of insulin-like growth factor-I and epidermal growth factor related pathways in animals treated with BMP-6. Significant upregulation of IGF-I and EGF expression in bones of BMP-6 treated mice was confirmed by quantitative PCR. To develop an in vitro model for evaluation of the effects of BMP-6 on cells of human origin, we cultured primary human osteoblasts. Treatment with rhBMP-6 accelerated cell differentiation as indicated by the formation of mineralised nodules by day 18 of culture versus 28-30 days in vehicle treated cultures. In addition, alkaline phosphatase gene expression and activity were dramatically increased upon BMP-6 treatment. Expression of IGF-I and EGF was upregulated in human osteoblast cells treated with BMP-6. These results collectively indicate that BMP-6 exerts its osteoinductive effect, at least in part, through IGF-I and EGF pathways, which can be observed both in a murine model of osteopenia and in human osteoblasts.
Nous avons récemment pu mettre en évidence que la BMP-6 (rhBMP-6), administrée de façon systématique, pouvait améliorer la restauration du capital osseux de modèles animaux avec ostéoporose. Nous avons conduit une expérimentation utilisant des souris ovarieactomisées traitées par BMP-6. L’analyse a montré qu’il y avait un apport d’insulin like growth factor et d’épidermal growth factor chez les animaux traités par BMP-6. Pour développer un modèle in vitro nous avons étudié l’effet de la BMP-6 sur les cellules de type ostéoplasties d’origine humaine. Le traitement par BMP-6 accélère la différenciation cellulaire au 18ème jour alors que normalement cette différence est notée aux alentours du 28ème et 30ème jour. De plus, l’expression du gène de la phosphatase alkaline et l’activité sont augmentées par le traitement par la BMP-6, de même en ce qui concerne l’IGF-1 et l’EGF. Ces résultats nous permettent de penser que le BMP-6 a un effet ostéo conducteur notamment pour les pathologies intéressant IGF-1 et EGF. Nous avons observé ces effets dans un modèle animal avec ostéoplastie et sur les ostéoblastes humains.
Figures

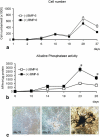

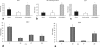
Similar articles
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-2 restores mineralization in glucocorticoid-inhibited MC3T3-E1 osteoblast cultures.J Bone Miner Res. 2003 Jul;18(7):1186-97. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.7.1186. J Bone Miner Res. 2003. PMID: 12854828
-
Follistatin restricts bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2 action on the differentiation of osteoblasts in fetal rat mandibular cells.J Bone Miner Res. 2004 Aug;19(8):1302-7. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.040408. Epub 2004 May 3. J Bone Miner Res. 2004. PMID: 15231018
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) enhances the osteogenic activity of bone morphogenetic protein-6 (BMP-6) in vitro and in vivo, and together have a stronger osteogenic effect than when IGF-1 is combined with BMP-2.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017 Jul;105(7):1867-1875. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36051. Epub 2017 Mar 29. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017. PMID: 28256809
-
Suppression of osteoblast-related genes during osteogenic differentiation of adipose tissue derived stromal cells.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017 Jan;45(1):33-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2016.10.006. Epub 2016 Oct 18. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017. PMID: 27842921
-
Growth factor control of bone mass.J Cell Biochem. 2009 Nov 1;108(4):769-77. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22322. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19718659 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chitosan-based double-faced barrier membrane coated with functional nanostructures and loaded with BMP-6.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019 Dec 12;31(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s10856-019-6331-x. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019. PMID: 31832785
-
In vitro differentiation and mineralization of dental pulp stem cells on enamel-like fluorapatite surfaces.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2012 Nov;18(11):821-30. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2011.0624. Epub 2012 Jun 25. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2012. PMID: 22563788 Free PMC article.
-
Biological aspects of bone, cartilage and tendon regeneration.Int Orthop. 2007 Dec;31(6):719-20. doi: 10.1007/s00264-007-0425-7. Epub 2007 Aug 18. Int Orthop. 2007. PMID: 17704918 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Promoting Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-driven Biomineralization and Periodontal Regeneration in Rats with Maxillary-Molar Defects using Injectable BMP-6 Hydrogel.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 8;8(1):114. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18415-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29311578 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in growth factor-containing 3D printed scaffolds in orthopedics.Biomed Eng Online. 2025 Feb 7;24(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12938-025-01346-z. Biomed Eng Online. 2025. PMID: 39920740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/8756-3282(95)00078-R', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/8756-3282(95)00078-r'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7544602', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7544602/'}]}
- Bagi C, van der Meulen M, Brommage R, Rosen D, Sommer A (1995) The effect of systemically administered rhIGF-I/IGFBP-3 complex on cortical bone strength and structure in ovariectomized rats. Bone 16:559–565 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8122528', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8122528/'}]}
- Baylink DJ, Finkelman RD, Mohan S (1993) Growth factors to stimulate bone formation. J Bone Miner Res 2:S565–S572 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1007/s00264-005-0045-z', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-005-0045-z'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2532081', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2532081/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16506027', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16506027/'}]}
- Bilic R, Simic P, Jelic M, Stern-Padovan R, Dodig D, van Meerdervoort HP, Martinovic S, Ivankovic D, Pecina M, Vukicevic S (2006) Osteogenic protein-1 (BMP-7) accelerates healing of scaphoid non-union with proximal pole sclerosis. Int Orthop 30:128–134 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8079660', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8079660/'}]}
- Franceschi RT, Iyer BS, Cui Y (1994) Effects of ascorbic acid on collagen matrix formation and osteoblast differentiation in murine MC3T3-E1 cells. J Bone Miner Res 9:843–854 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11769970', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11769970/'}]}
- Jelic M, Pecina M, Haspl M, Kos J, Taylor K, Maticic D, McCartney J, Yin S, Rueger D, Vukicevic S (2001) Regeneration of articular cartilage chondral defects by osteogenic protein-1 (bone morphogenetic protein-7) in sheep. Growth Factors 19:101–113 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

