Protein phosphatase-1 is a novel regulator of the interaction between IRBIT and the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor
- PMID: 17635105
- PMCID: PMC2049018
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070361
Protein phosphatase-1 is a novel regulator of the interaction between IRBIT and the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor
Abstract
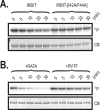
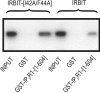
IRBIT is an IP3R [IP3 (inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate) receptor]-binding protein that competes with IP3 for binding to the IP3R. Phosphorylation of IRBIT is essential for the interaction with the IP3R. The unique N-terminal region of IRBIT, residues 1-104 for mouse IRBIT, contains a PEST (Pro-Glu-Ser-Thr) domain with many putative phosphorylation sites. In the present study, we have identified a well-conserved PP1 (protein phosphatase-1)-binding site preceeding this PEST domain which enabled the binding of PP1 to IRBIT both in vitro and in vivo. IRBIT emerged as a mediator of its own dephosphorylation by associated PP1 and, hence, as a novel substrate specifier for PP1. Moreover, IRBIT-associated PP1 specifically dephosphorylated Ser68 of IRBIT. Phosphorylation of Ser68 was required for subsequent phosphorylation of Ser71 and Ser74, but the latter two sites were not targeted by PP1. We found that phosphorylation of Ser71 and Ser74 were sufficient to enable inhibition of IP3 binding to the IP3R by IRBIT. Finally, we have shown that mutational inactivation of the docking site for PP1 on IRBIT increased the affinity of IRBIT for the IP3R. This pinpoints PP1 as a key player in the regulation of IP3R-controlled Ca2+ signals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Binding of IRBIT to the IP3 receptor: determinants and functional effects.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Apr 28;343(1):49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.02.119. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. PMID: 16527252
-
IRBIT suppresses IP3 receptor activity by competing with IP3 for the common binding site on the IP3 receptor.Mol Cell. 2006 Jun 23;22(6):795-806. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.05.017. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16793548
-
TRPC channel interactions with calmodulin and IP3 receptors.Novartis Found Symp. 2004;258:44-58; discussion 58-62, 98-102, 263-6. Novartis Found Symp. 2004. PMID: 15104175
-
The IRBIT domain adds new functions to the AHCY family.Bioessays. 2008 Jul;30(7):642-52. doi: 10.1002/bies.20772. Bioessays. 2008. PMID: 18536033 Review.
-
The IP3 receptor/Ca2+ channel and its cellular function.Biochem Soc Symp. 2007;(74):9-22. doi: 10.1042/BSS0740009. Biochem Soc Symp. 2007. PMID: 17233576 Review.
Cited by
-
IRBIT coordinates epithelial fluid and HCO3- secretion by stimulating the transporters pNBC1 and CFTR in the murine pancreatic duct.J Clin Invest. 2009 Jan;119(1):193-202. doi: 10.1172/JCI36983. Epub 2008 Dec 1. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19033647 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple acid-base and electrolyte disturbances upregulate NBCn1, NBCn2, IRBIT and L-IRBIT in the mTAL.J Physiol. 2020 Aug;598(16):3395-3415. doi: 10.1113/JP279009. Epub 2020 May 30. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32359081 Free PMC article.
-
IRBITs, signaling molecules of great functional diversity.Pflugers Arch. 2025 Aug;477(8):1007-1036. doi: 10.1007/s00424-025-03095-3. Epub 2025 May 30. Pflugers Arch. 2025. PMID: 40445299 Review.
-
IRBIT Interacts with the Catalytic Core of Phosphatidylinositol Phosphate Kinase Type Iα and IIα through Conserved Catalytic Aspartate Residues.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 28;10(10):e0141569. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141569. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26509711 Free PMC article.
-
IRBIT: it is everywhere.Neurochem Res. 2011 Jul;36(7):1166-74. doi: 10.1007/s11064-010-0353-6. Epub 2010 Dec 9. Neurochem Res. 2011. PMID: 21152975 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993;361:315–325. - PubMed
-
- Devogelaere B., Verbert L., Parys J. B., Missiaen L., De Smedt H. The complex regulatory function of the ligand-binding domain of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. Cell Calcium. 2007. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2007.04.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Verbert L., Devogelaere B., Parys J. B., Missiaen L., Bultynck G., De Smedt H. Proteolytic mechanisms leading to disturbed Ca2+ signalling in apoptotic cell death. Calcium Binding Proteins. 2007;2:21–29.
-
- Krizanova O., Ondrias K. The inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor: transcriptional regulation and modulation by phosphorylation. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2003;22:295–311. - PubMed
-
- Patterson R. L., Boehning D., Snyder S. H. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors as signal integrators. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004;73:437–465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

