The cAMP pathway is important for controlling the morphological switch to the pathogenic yeast form of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
- PMID: 17635191
- PMCID: PMC2064555
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05824.x
The cAMP pathway is important for controlling the morphological switch to the pathogenic yeast form of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
Abstract
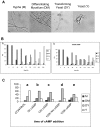
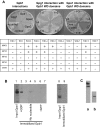
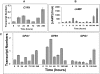
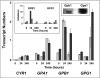
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis is a human pathogenic fungus that switches from a saprobic mycelium to a pathogenic yeast. Consistent with the morphological transition being regulated by the cAMP-signalling pathway, there is an increase in cellular cAMP levels both transiently at the onset (< 24 h) and progressively in the later stages (> 120 h) of the transition to the yeast form, and this transition can be modulated by exogenous cAMP. We have cloned the cyr1 gene encoding adenylate cyclase (AC) and established that its transcript levels correlate with cAMP levels. In addition, we have cloned the genes encoding three Galpha (Gpa1-3), Gbeta (Gpb1) and Ggamma (Gpg1) G proteins. Gpa1 and Gpb1 interact with one another and the N-terminus of AC, but neither Gpa2 nor Gpa3 interacted with Gpb1 or AC. The interaction of Gpa1 with Gpb1 was blocked by GTP, but its interaction with AC was independent of bound nucleotide. The transcript levels for gpa1, gpb1 and gpg1 were similar in mycelium, but there was a transient excess of gpb1 during the transition, and an excess of gpa1 in yeast. We have interpreted our findings in terms of a novel signalling mechanism in which the activity of AC is differentially modulated by Gpa1 and Gpb1 to maintain the signal over the 10 days needed for the morphological switch.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Noncanonical Gβ Gib2 is a scaffolding protein promoting cAMP signaling through functions of Ras1 and Cac1 proteins in Cryptococcus neoformans.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 2;289(18):12202-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.537183. Epub 2014 Mar 21. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24659785 Free PMC article.
-
Heterotrimeric G-gamma 1 (Gpg1) participates with G-beta 1 (Gpb1) in the induction of hyphal growth and virulence via the PKA pathway in Mucor lusitanicus.Fungal Genet Biol. 2025 May;178:103974. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2025.103974. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Fungal Genet Biol. 2025. PMID: 40049442
-
Gib2, a novel Gbeta-like/RACK1 homolog, functions as a Gbeta subunit in cAMP signaling and is essential in Cryptococcus neoformans.J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 27;281(43):32596-605. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602768200. Epub 2006 Sep 1. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16950773
-
Novel sensing mechanisms and targets for the cAMP-protein kinase A pathway in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Sep;33(5):904-18. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01538.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10476026 Review.
-
Functional genome of the human pathogenic fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2005 Sep 1;45(3):369-81. doi: 10.1016/j.femsim.2005.05.013. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16061364 Review.
Cited by
-
Divergent Protein Kinase A isoforms co-ordinately regulate conidial germination, carbohydrate metabolism and virulence in Aspergillus fumigatus.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Feb;79(4):1045-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07509.x. Epub 2011 Jan 6. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21210869 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP Signaling Regulates Synchronised Growth of Symbiotic Epichloë Fungi with the Host Grass Lolium perenne.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Oct 27;7:1546. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01546. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27833620 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-independent signal pathways stimulate hyphal morphogenesis in Candida albicans.Mol Microbiol. 2017 Mar;103(5):764-779. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13588. Epub 2016 Dec 19. Mol Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27888610 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Wall Synthesis, Development of Hyphae and Metabolic Pathways Are Processes Potentially Regulated by MicroRNAs Produced Between the Morphological Stages of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis.Front Microbiol. 2018 Dec 11;9:3057. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03057. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30619144 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of transcription of multiple genes during mycelia transition to yeast cells of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis reveals insights to fungal differentiation and pathogenesis.Mycopathologia. 2008 Apr-May;165(4-5):259-73. doi: 10.1007/s11046-007-9078-8. Mycopathologia. 2008. PMID: 18777633
References
-
- Batlle M, Lu A, Green DA, Xue Y, Hirsch JP. Krh1p and Krh2p act downstream of the Gpa2p G (alpha) subunit to negatively regulate haploid invasive growth. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:701–710. - PubMed
-
- Bennett RJ, Johnson AD. The role of nutrient regulation and the Gpa2 protein in the mating pheromone response of C. albicans. Mol Microbiol. 2006;62:100–119. - PubMed
-
- Borges-Walmsley MI, Walmsley AR. cAMP signaling in pathogenic fungi: control of dimorphic switching and pathogenicity. Trends Microbiol. 2000;8:133–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

