Mammalian heparanase: what is the message?
- PMID: 17635638
- PMCID: PMC3922351
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00039.x
Mammalian heparanase: what is the message?
Abstract
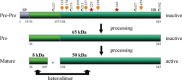
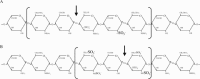
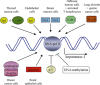
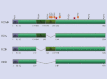
Heparan sulphate proteoglycans are ubiquitous macromolecules of cell surfaces and extracellular matrices. Numerous extracellular matrix proteins, growth factors, morphogens, cytokines, chemokines and coagulation factors are bound and regulated by heparan sulphate. Degradation of heparan sulphate thus potentially profoundly affects cell and tissue function. Although there is evidence that several heparan sulphate-degrading endoglucuronidases (heparanases) might exist, so far only one transcript encoding a functional heparanase has been identified: heparanase-1. In the first part of this review, we discuss the current knowledge about heparan sulphate proteoglycans and the functional importance of their versatile interactions. In the second part, we summarize recent findings that have contributed to the characterization of heparanase-1, focusing on the molecular properties, working mechanism, substrate specificity, expression pattern, cellular activation and localization of this enzyme. Additionally, we review data implicating heparanase-1 in several normal and pathological processes, focusing on tumour metastasis and angiogenesis, and on evidence for a potentially direct signalling function of the molecule. In that context, we also briefly discuss heparanase-2, an intriguing close homologue of heparanase-1, for which, so far, no heparan sulphate-degrading activity could be demonstrated.
Figures


References
-
- Bernfield M, Gotte M, Park PW, Reizes O, Fitzgerald ML, Lincecum J, Zako M. Functions of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:729–77. - PubMed
-
- Esko JD, Selleck SB. Order out of chaos: assembly of ligand binding sites in heparan sulfate. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:435–71. - PubMed
-
- Chen RL, Lander AD. Mechanisms underlying preferential assembly of heparan sulfate on glypican-1. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:7507–17. - PubMed
-
- Esko JD, Zhang L. Influence of core protein sequence on glycosaminoglycan assembly. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1996;6:663–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

