Serpins in thrombosis, hemostasis and fibrinolysis
- PMID: 17635716
- PMCID: PMC2670448
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02516.x
Serpins in thrombosis, hemostasis and fibrinolysis
Abstract
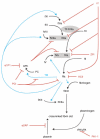
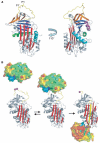
Hemostasis and fibrinolysis, the biological processes that maintain proper blood flow, are the consequence of a complex series of cascading enzymatic reactions. Serine proteases involved in these processes are regulated by feedback loops, local cofactor molecules, and serine protease inhibitors (serpins). The delicate balance between proteolytic and inhibitory reactions in hemostasis and fibrinolysis, described by the coagulation, protein C and fibrinolytic pathways, can be disrupted, resulting in the pathological conditions of thrombosis or abnormal bleeding. Medicine capitalizes on the importance of serpins, using therapeutics to manipulate the serpin-protease reactions for the treatment and prevention of thrombosis and hemorrhage. Therefore, investigation of serpins, their cofactors, and their structure-function relationships is imperative for the development of state-of-the-art pharmaceuticals for the selective fine-tuning of hemostasis and fibrinolysis. This review describes key serpins important in the regulation of these pathways: antithrombin, heparin cofactor II, protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor, alpha(1)-protease inhibitor, protein C inhibitor, alpha(2)-antiplasmin and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. We focus on the biological function, the important structural elements, their known non-hemostatic roles, the pathologies related to deficiencies or dysfunction, and the therapeutic roles of specific serpins.
Figures

References
-
- Bode W. The structure of thrombin: a janus-headed proteinase. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006;32(Suppl 1):16–31. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman M, Monroe DM. Coagulation 2006: a modern view of hemostasis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2007;21:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Von Hundelshausen P, Weber C. Platelets as immune cells: bridging inflammation and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2007;100:27–40. - PubMed
-
- Leger AJ, Covic L, Kuliopulos A. Protease-activated receptors in cardiovascular diseases. Circulation. 2006;114:1070–7. - PubMed
-
- Harker LA, Hanson SR, Runge MS. Thrombin hypothesis of thrombus generation and vascular lesion formation. Am J Cardiol. 1995;75:12B–7B. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

