Role for sagA and siaA in quorum sensing and iron regulation in Streptococcus pyogenes
- PMID: 17635862
- PMCID: PMC2044554
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01824-06
Role for sagA and siaA in quorum sensing and iron regulation in Streptococcus pyogenes
Abstract
Streptococcus pyogenes is a ubiquitous and versatile pathogen that causes a variety of infections with a wide range of severity. The versatility of this organism is due in part to its capacity to regulate virulence gene expression in response to the many environments that it encounters during an infection. We analyzed the expression of two potential virulence factors, sagA and siaA (also referred to as pel and htsA, respectively), in response to conditions of varying cell densities and iron concentrations. The sagA gene was up-regulated in conditioned medium from a wild-type strain but not from sagA-deficient mutants, and the gene was also up-regulated in the presence of streptolysin S (SLS), the gene product of sagA, thus indicating that this gene or its product is involved in density-dependent regulation of S. pyogenes. By comparison, siaA responded in a manner consistent with a role in iron acquisition since it was up-regulated under iron-restricted conditions. Although siaA expression was also up-regulated in the presence of SLS and in conditioned media from both wild-type and sagA-deficient mutants, this up-regulation was not growth phase dependent. We conclude that sagA encodes a quorum-sensing signaling molecule, likely SLS, and further support the notion that siaA is likely involved in iron acquisition.
Figures

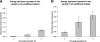

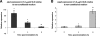
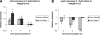
Similar articles
-
Streptolysin S-like virulence factors: the continuing sagA.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 Aug 8;9(9):670-81. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2624. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21822292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of sagA, siaA and scpC by SilCR, a putative signaling peptide of Streptococcus pyogenes.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2008 Dec;289(2):119-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01375.x. Epub 2008 Oct 29. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2008. PMID: 19016875
-
Linking the nutritional status of Streptococcus pyogenes to alteration of transcriptional gene expression: the action of CodY and RelA.Int J Med Microbiol. 2006 Aug;296(4-5):259-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.11.008. Epub 2006 Mar 13. Int J Med Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16531115
-
Synthesis of group A streptococcal virulence factors is controlled by a regulatory RNA molecule.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Sep;53(5):1515-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04222.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15387826
-
Streptococcus iniae beta-hemolysin streptolysin S is a virulence factor in fish infection.Dis Aquat Organ. 2007 Jun 7;76(1):17-26. doi: 10.3354/dao076017. Dis Aquat Organ. 2007. PMID: 17718161
Cited by
-
Functional analysis of the group A streptococcal luxS/AI-2 system in metabolism, adaptation to stress and interaction with host cells.BMC Microbiol. 2008 Oct 30;8:188. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-8-188. BMC Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18973658 Free PMC article.
-
CovRS-Regulated Transcriptome Analysis of a Hypervirulent M23 Strain of Group A Streptococcus pyogenes Provides New Insights into Virulence Determinants.J Bacteriol. 2015 Oct;197(19):3191-205. doi: 10.1128/JB.00511-15. Epub 2015 Jul 27. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26216843 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of streptokinase expression by CovR/S in Streptococcus pyogenes: CovR acts through a single high-affinity binding site.Microbiology (Reading). 2009 Feb;155(Pt 2):566-575. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.024620-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2009. PMID: 19202105 Free PMC article.
-
Streptolysin S-like virulence factors: the continuing sagA.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 Aug 8;9(9):670-81. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2624. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21822292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory role of acyl homoserine lactones in hemolytic activity and viability of Streptococcus pyogenes M6 S165.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 17;7:44902. doi: 10.1038/srep44902. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28303956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banerjee, S., and J. N. Hansen. 1988. Structure and expression of a gene encoding the precursor of subtilin, a small protein antibiotic. J. Biol. Chem. 263:9508-9514. - PubMed
-
- Cotter, P. D., C. Hill, and R. P. Ross. 2005. Bacteriocins: developing innate immunity for food. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3:777-788. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

