G protein-independent Ras/PI3K/F-actin circuit regulates basic cell motility
- PMID: 17635933
- PMCID: PMC2064438
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200611138
G protein-independent Ras/PI3K/F-actin circuit regulates basic cell motility
Abstract
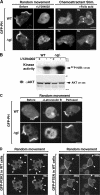
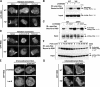
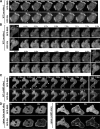
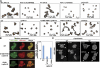
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)gamma and Dictyostelium PI3K are activated via G protein-coupled receptors through binding to the Gbetagamma subunit and Ras. However, the mechanistic role(s) of Gbetagamma and Ras in PI3K activation remains elusive. Furthermore, the dynamics and function of PI3K activation in the absence of extracellular stimuli have not been fully investigated. We report that gbeta null cells display PI3K and Ras activation, as well as the reciprocal localization of PI3K and PTEN, which lead to local accumulation of PI(3,4,5)P(3). Simultaneous imaging analysis reveals that in the absence of extracellular stimuli, autonomous PI3K and Ras activation occur, concurrently, at the same sites where F-actin projection emerges. The loss of PI3K binding to Ras-guanosine triphosphate abolishes this PI3K activation, whereas prevention of PI3K activity suppresses autonomous Ras activation, suggesting that PI3K and Ras form a positive feedback circuit. This circuit is associated with both random cell migration and cytokinesis and may have initially evolved to control stochastic changes in the cytoskeleton.
Figures
References
-
- Comer, F.I., C.K. Lippincott, J.J. Masbad, and C.A. Parent. 2005. The PI3K-mediated activation of CRAC independently regulates adenylyl cyclase activation and chemotaxis. Curr. Biol. 15:134–139. - PubMed
-
- Condeelis, J., and J.E. Segall. 2003. Intravital imaging of cell movement in tumours. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 3:921–930. - PubMed
-
- Engelman, J.A., J. Luo, and L.C. Cantley. 2006. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 7:606–619. - PubMed
-
- Funamoto, S., R. Meili, S. Lee, L. Parry, and R. Firtel. 2002. Spatial and temporal regulation of 3-phosphoinositides by PI 3-kinase and PTEN mediates chemotaxis. Cell. 109:611–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM037830/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM080370/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM037830/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM034933/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM28007/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071920/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM028007/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM071920/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM24279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM028007/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM34933/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM024279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM06847/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

