GDI-1 phosphorylation switch at serine 96 induces RhoA activation and increased endothelial permeability
- PMID: 17636025
- PMCID: PMC2099605
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00523-07
GDI-1 phosphorylation switch at serine 96 induces RhoA activation and increased endothelial permeability
Abstract
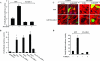
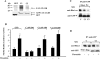
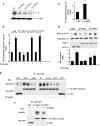
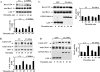
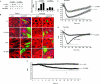
We identified the GDI-1-regulated mechanism of RhoA activation from the Rho-GDI-1 complex and its role in mediating increased endothelial permeability. Thrombin stimulation failed to induce RhoA activation and actin stress fiber formation in human pulmonary arterial endothelial cells transduced with full-length GDI-1. Expression of a GDI-1 mutant form (C-GDI) containing the C terminus (aa 69 to 204) also prevented RhoA activation, whereas further deletions failed to alter RhoA activation. We observed that protein kinase Calpha-mediated phosphorylation of the C terminus of GDI-1 at Ser96 reduced the affinity of GDI-1 for RhoA and thereby enabled RhoA activation. Rendering GDI-1 phosphodefective with a Ser96 --> Ala substitution rescued the inhibitory activity of GDI-1 toward RhoA but did not alter the thrombin-induced activation of other Rho GTPases, i.e., Rac1 and Cdc42. Phosphodefective mutant GDI-1 also suppressed myosin light chain phosphorylation, actin stress fiber formation, and the increased endothelial permeability induced by thrombin. In contrast, expressing the phospho-mimicking mutant S96D-GDI-1 protein induced RhoA activity and increased endothelial permeability independently of thrombin stimulation. These results demonstrate the crucial role of the phosphorylation of the C terminus of GDI-1 at S96 in selectively activating RhoA. Inhibiting GDI-1 phosphorylation at S96 is a potential therapeutic target for modulating RhoA activity and thus preventing the increase in endothelial permeability associated with vascular inflammation.
Figures
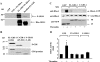
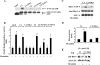
References
-
- Chikumi, H., J. Vázquez-Prado, J.-M. Servitja, H. Miyazaki, and J. S. Gutkind. 2002. Potent activation of RhoA by Gαq and Gq-coupled receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 277:27130-27134. - PubMed
-
- Coughlin, S. R. 2000. Thrombin signalling and protease-activated receptors. Nature 407:258-264. - PubMed
-
- DerMardirossian, C., and G. M. Bokoch. 2005. GDIs: central regulatory molecules in Rho GTPase activation. Trends Cell Biol. 15:356-363. - PubMed
-
- DerMardirossian, C., A. Schnelzer, and G. M. Bokoch. 2004. Phosphorylation of RhoGDI by Pak1 mediates dissociation of Rac GTPase. Mol. Cell 15:117-127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
