FRET imaging in living maize cells reveals that plasma membrane aquaporins interact to regulate their subcellular localization
- PMID: 17636130
- PMCID: PMC1941474
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0701180104
FRET imaging in living maize cells reveals that plasma membrane aquaporins interact to regulate their subcellular localization
Abstract
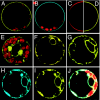
Zea mays plasma membrane intrinsic proteins (ZmPIPs) fall into two groups, ZmPIP1s and ZmPIP2s, that exhibit different water channel activities when expressed in Xenopus oocytes. ZmPIP1s are inactive, whereas ZmPIP2s induce a marked increase in the membrane osmotic water permeability coefficient, P(f). We previously showed that, in Xenopus oocytes, ZmPIP1;2 and ZmPIP2;1 interact to increase the cell P(f). Here, we report the localization and interaction of ZmPIP1s and ZmPIP2s in living maize cells. ZmPIPs were fused to monomeric yellow fluorescent protein and/or monomeric cyan fluorescent protein and expressed transiently in maize mesophyll protoplasts. When expressed alone, ZmPIP1 fusion proteins were retained in the endoplasmic reticulum, whereas ZmPIP2s were found in the plasma membrane. Interestingly, when coexpressed with ZmPIP2s, ZmPIP1s were relocalized to the plasma membrane. Using FRET/fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy, we demonstrated that this relocalization results from interaction between ZmPIP1s and ZmPIP2s. Immunoprecipitation experiments provided additional evidence for the association of ZmPIP1;2 and ZmPIP2;1 in maize roots and suspension cells. These data suggest that PIP1-PIP2 interaction is required for in planta PIP1 trafficking to the plasma membrane to modulate plasma membrane permeability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

