Interaction of estrogen receptor alpha with proliferating cell nuclear antigen
- PMID: 17636311
- PMCID: PMC1976446
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm533
Interaction of estrogen receptor alpha with proliferating cell nuclear antigen
Abstract
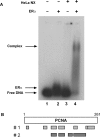
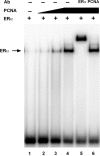
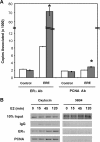
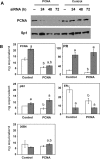
The ability of estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) to modulate gene expression is influenced by the recruitment of a host of co-regulatory proteins to target genes. To further understand how estrogen-responsive genes are regulated, we have isolated and identified proteins associated with ERalpha when it is bound to DNA containing the consensus estrogen response element (ERE). One of the proteins identified in this complex, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), is required for DNA replication and repair. We show that PCNA interacts with ERalpha in the absence and in the presence of DNA, enhances the interaction of ERalpha with ERE-containing DNA, and associates with endogenous estrogen-responsive genes. Interestingly, rather than altering hormone responsiveness of endogenous, estrogen-responsive genes, PCNA increases the basal expression of these genes. Our studies suggest that in addition to serving as a platform for the recruitment of DNA replication and repair proteins, PCNA may serve as a platform for transcription factors involved in regulating gene expression.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Two estrogen response element sequences near the PCNA gene are not responsible for its estrogen-enhanced expression in MCF7 cells.PLoS One. 2008;3(10):e3523. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003523. Epub 2008 Oct 24. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18949048 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor α mediates proliferation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells via a p21/PCNA/E2F1-dependent pathway.FEBS J. 2014 Feb;281(3):927-42. doi: 10.1111/febs.12658. Epub 2014 Jan 2. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24283290
-
The deoxyribonucleic acid repair protein flap endonuclease-1 modulates estrogen-responsive gene expression.Mol Endocrinol. 2007 Jul;21(7):1569-80. doi: 10.1210/me.2006-0519. Epub 2007 May 8. Mol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17488975
-
Genomic responses from the estrogen-responsive element-dependent signaling pathway mediated by estrogen receptor alpha are required to elicit cellular alterations.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 29;284(22):15277-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M900365200. Epub 2009 Mar 24. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19321454 Free PMC article.
-
Protein disulfide isomerase serves as a molecular chaperone to maintain estrogen receptor alpha structure and function.Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Sep;20(9):1982-95. doi: 10.1210/me.2006-0006. Epub 2006 May 11. Mol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16690750
Cited by
-
Estrogen signaling and the DNA damage response in hormone dependent breast cancers.Front Oncol. 2014 May 14;4:106. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00106. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24860786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol, 4' Acetoxy Resveratrol, R-equol, Racemic Equol or S-equol as Cosmeceuticals to Improve Dermal Health.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 3;18(6):1193. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061193. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28587197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two estrogen response element sequences near the PCNA gene are not responsible for its estrogen-enhanced expression in MCF7 cells.PLoS One. 2008;3(10):e3523. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003523. Epub 2008 Oct 24. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18949048 Free PMC article.
-
PCNA interacts with Prox1 and represses its transcriptional activity.Mol Vis. 2008;14:2076-86. Epub 2008 Nov 17. Mol Vis. 2008. PMID: 19023449 Free PMC article.
-
A progesterone receptor co-activator (JDP2) mediates activity through interaction with residues in the carboxyl-terminal extension of the DNA binding domain.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24415-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.003244. Epub 2009 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19553667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frasor J, Danes JM, Komm B, Chang KC, Lyttle CR, Katzenellenbogen BS. Profiling of estrogen up- and down-regulated gene expression in human breast cancer cells: insights into gene networks and pathways underlying estrogenic control of proliferation and cell phenotype. Endocrinology. 2003;144:4562–4574. - PubMed
-
- Frasor J, Stossi F, Danes JM, Komm B, Lyttle CR, Katzenellenbogen BS. Selective estrogen receptor modulators: discrimination of agonistic versus antagonistic activities by gene expression profiling in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1522–1533. - PubMed
-
- Korach KS. Insights from the study of animals lacking functional estrogen receptor. Science. 1994;266:1524–1527. - PubMed
-
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989;56:335–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

