Interaction of estrogen receptor alpha with proliferating cell nuclear antigen
- PMID: 17636311
- PMCID: PMC1976446
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm533
Interaction of estrogen receptor alpha with proliferating cell nuclear antigen
Abstract
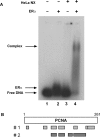
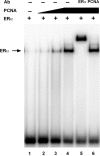
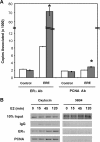
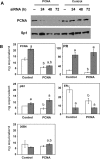
The ability of estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) to modulate gene expression is influenced by the recruitment of a host of co-regulatory proteins to target genes. To further understand how estrogen-responsive genes are regulated, we have isolated and identified proteins associated with ERalpha when it is bound to DNA containing the consensus estrogen response element (ERE). One of the proteins identified in this complex, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), is required for DNA replication and repair. We show that PCNA interacts with ERalpha in the absence and in the presence of DNA, enhances the interaction of ERalpha with ERE-containing DNA, and associates with endogenous estrogen-responsive genes. Interestingly, rather than altering hormone responsiveness of endogenous, estrogen-responsive genes, PCNA increases the basal expression of these genes. Our studies suggest that in addition to serving as a platform for the recruitment of DNA replication and repair proteins, PCNA may serve as a platform for transcription factors involved in regulating gene expression.
Figures


References
-
- Frasor J, Danes JM, Komm B, Chang KC, Lyttle CR, Katzenellenbogen BS. Profiling of estrogen up- and down-regulated gene expression in human breast cancer cells: insights into gene networks and pathways underlying estrogenic control of proliferation and cell phenotype. Endocrinology. 2003;144:4562–4574. - PubMed
-
- Frasor J, Stossi F, Danes JM, Komm B, Lyttle CR, Katzenellenbogen BS. Selective estrogen receptor modulators: discrimination of agonistic versus antagonistic activities by gene expression profiling in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1522–1533. - PubMed
-
- Korach KS. Insights from the study of animals lacking functional estrogen receptor. Science. 1994;266:1524–1527. - PubMed
-
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989;56:335–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

