Detection of phosphodiester adducts formed by the reaction of benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide with 2'-deoxynucleotides using collision-induced dissociation electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 17636312
- PMCID: PMC1976470
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm526
Detection of phosphodiester adducts formed by the reaction of benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide with 2'-deoxynucleotides using collision-induced dissociation electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
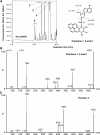
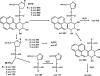
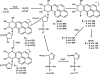
In this study, we investigated the products formed following the reaction of benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide (B[a]PDE) with 2'-deoxynucleoside 3'-monophosphates. The B[a]PDE plus 2'-deoxynucleotide reaction mixtures were purified using solid phase extraction (SPE) and subjected to HPLC with fluorescence detection. Fractions corresponding to reaction product peaks were collected and desalted using SPE prior to analysis for the presence of molecular ions corresponding to m/z 648, 632, 608 and 623 [M-H]- consistent with B[a]PDE adducted (either on the base or phosphate group) 2'-deoxynucleotides of guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine, respectively, using LC-ESI-MS/MS collision-induced dissociation (CID). Reaction products were identified having CID product ion spectra containing product ions at m/z 452, 436 and 412 [(B[a]Ptriol+base)-H]-, resulting from cleavage of the glycosidic bond between the 2'-deoxyribose and base, corresponding to B[a]PDE adducts of guanine, adenine and cytosine, respectively. Further reaction products were identified having unique CID product ion spectra characteristic of B[a]PDE adduct formation with the phosphate group of the 2'-deoxynucleotide. The presence of product ions at m/z 399 and 497 were observed for all four 2'-deoxynucleotides, corresponding to [(B[a]Ptriol+phosphate)-H]- and [(2'-deoxyribose+phosphate+B[a]Ptriol)-H]-, respectively. In conclusion, this investigation provides the first direct evidence for the formation of phosphodiester adducts by B[a]PDE following reaction with 2'-deoxynucleotides.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Analysis of benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide-DNA adducts by capillary zone electrophoresis- electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry in conjunction with sample stacking.Electrophoresis. 2002 Dec;23(24):4092-103. doi: 10.1002/elps.200290026. Electrophoresis. 2002. PMID: 12481265
-
Selective digestion and novel cleanup techniques for detection of benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide-DNA adducts by capillary electrophoresis/mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2004;18(14):1541-7. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1516. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2004. PMID: 15282777
-
The influence of cytosine methylation on the chemoselectivity of benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide-oligonucleotide adducts determined using nanoLC/MS/MS.J Mass Spectrom. 2009 Aug;44(8):1241-8. doi: 10.1002/jms.1605. J Mass Spectrom. 2009. PMID: 19536795 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide-DNA adducts at specific guanines within K-ras and p53 gene sequences: stable isotope-labeling mass spectrometry approach.Biochemistry. 2002 Jul 30;41(30):9535-44. doi: 10.1021/bi025540i. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12135376
-
Analysis of DNA and protein adducts of benzo[a]pyrene in human tissues using structure-specific methods.Mutat Res. 2003 Jan;543(1):17-30. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5742(02)00068-6. Mutat Res. 2003. PMID: 12510015 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA adducts: Formation, biological effects, and new biospecimens for mass spectrometric measurements in humans.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2020 Mar;39(1-2):55-82. doi: 10.1002/mas.21570. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2020. PMID: 29889312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Technologies in Mass Spectrometry-Based DNA Adductomics.High Throughput. 2019 May 14;8(2):13. doi: 10.3390/ht8020013. High Throughput. 2019. PMID: 31091740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HPLC-UV, MALDI-TOF-MS and ESI-MS/MS analysis of the mechlorethamine DNA crosslink at a cytosine-cytosine mismatch pair.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020745. Epub 2011 Jun 6. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21673963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannon P, Verly W. Alkylation of phosphates and stability of phosphate triesters in DNA. Eur. J. Biochem. 1972;31:103–111. - PubMed
-
- Shooter KV. DNA phosphotriesters as indicators of cumulative carcinogen induced damage. Nature. 1978;274:612–614. - PubMed
-
- Beranek DT. Distribution of methyl and ethyl adducts following alkylation with monofunctional alkylating agents. Mutat. Res. 1990;231:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Koreeda M, Moore PD, Yagi H, Yeh HJC, Jerina DM. Alkylation of polyguanylic acid at the 2-amino group and phosphate by the potent mutagen (±)-7β,8α-dihydroxy-9β, 10β-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976;98:6720–6722. - PubMed
-
- Shooter KV, Slade TA. The stability of methyl and ethyl phosphotriesters in DNA in vivo. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1977;19:353–361. - PubMed

