Huperzine A reverses cholinergic and monoaminergic dysfunction induced by bilateral nucleus basalis magnocellularis injection of beta-amyloid peptide (1-40) in rats
- PMID: 17636406
- PMCID: PMC11515454
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-007-9158-9
Huperzine A reverses cholinergic and monoaminergic dysfunction induced by bilateral nucleus basalis magnocellularis injection of beta-amyloid peptide (1-40) in rats
Abstract
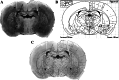
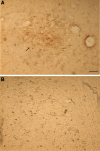
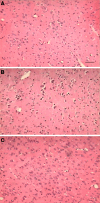
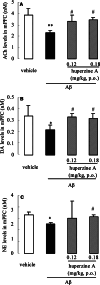
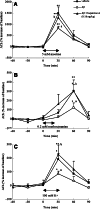
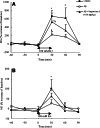
(1) Huperzine A, a promising therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's disease (AD), was tested for its effects on cholinergic and monoaminergic dysfunction induced by injecting beta-amyloid peptide-(1-40) into nucleus basalis magnocellularis of the rat. (2) Bilateral injection of 10 microg beta-amyloid peptide-(1-40) into nucleus basalis magnocellularis produced local deposits of amyloid plaque and functional abnormalities detected by microdialysis. In medial prefrontal cortex, reductions in the basal levels and stimulated release of acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine were observed. However, oral huperzine A (0.18 mg/kg, once daily for 21 consecutive days) markedly reduced morphologic abnormalities at the injection site in rats infused with beta-amyloid peptide-(1-40). Likewise, this treatment ameliorated the beta-amyloid peptide-(1-40)-induced deficits in extracellular acetylcholine, dopamine, and norepinephrine (though not 5-hydroxytryptamine) in medial prefrontal cortex, and lessened the reduction in nicotine or methoctramine-stimulated release of acetylcholine and K(+)-evoked releases of acetylcholine and dopamine. (3) The present results provide the first direct evidence that huperzine A acts to oppose neurotoxic effects of beta-amyloid peptide on cholinergic, dopaminergic, and noradrenergic systems of the rat forebrain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rivastigmine antagonizes deficits in prepulse inhibition induced by selective immunolesioning of cholinergic neurons in nucleus basalis magnocellularis.Neuroscience. 2002;114(1):91-8. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00234-8. Neuroscience. 2002. PMID: 12207957
-
Comparative studies of huperzine A, donepezil, and rivastigmine on brain acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine levels in freely-moving rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006 Sep;27(9):1127-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2006.00411.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006. PMID: 16923332
-
Huperzine A attenuates cognitive dysfunction and neuronal degeneration caused by beta-amyloid protein-(1-40) in rat.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Jun 15;421(3):149-56. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01030-5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11516430
-
Selective immunolesioning of cholinergic neurons in nucleus basalis magnocellularis impairs prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle.Neuroscience. 2001;108(2):299-305. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00413-4. Neuroscience. 2001. PMID: 11734362
-
beta-Amyloid excitotoxicity in rat magnocellular nucleus basalis. Effect of cortical deafferentation on cerebral blood flow regulation and implications for Alzheimer's disease.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000 Apr;903:374-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06389.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 10818528 Review.
Cited by
-
Huperzine A for mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD008827. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008827.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235666 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cortical acetylcholine release: insights from in vivo microdialysis studies.Behav Brain Res. 2011 Aug 10;221(2):527-36. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.02.022. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Behav Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 20170686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Synopsis of Multitarget Potential Therapeutic Effects of Huperzine A in Diverse Pathologies-Emphasis on Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis.Neurochem Res. 2022 May;47(5):1166-1182. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03530-2. Epub 2022 Feb 5. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 35122609 Review.
-
The effects of huperzine A and IDRA 21 on visual recognition memory in young macaques.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Jun;60(7-8):1262-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.12.018. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21185313 Free PMC article.
-
Disease-Modifying Activity of Huperzine A on Alzheimer's Disease: Evidence from Preclinical Studies on Rodent Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 3;23(23):15238. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315238. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499562 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abe E, Casamenti F, Giovannelli L, Scali C, Pepeu G (1994) Administration of amyloid β-peptides into the medial septum of rats decreases acetylcholine release from hippocampus in vivo. Brain Res 636:162–164 - PubMed
-
- Barili P, De Carolis G, Zaccheo D, Amenta F (1998) Sensitivity to ageing of the limbic dopaminergic system: a review. Mech Ageing Dev 106:57–92 - PubMed
-
- Bartus RT III, Dean RL, Beer B, Lippa S (1982) The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science 217:408–414 - PubMed
-
- Busciglio J, Lorezo A, Yankner BA (1992) Methodological variables in the assessment of β-amyloid neurotoxicity. Neurobiol Aging 13:609–612 - PubMed
-
- Coyle JT, Price DL, DeLong MR (1983) Alzheimer’s disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science 219:1184–1190 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

