Thioridazine for schizophrenia
- PMID: 17636691
- PMCID: PMC6718212
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001944.pub2
Thioridazine for schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Thioridazine is an antipsychotic that can still be used for schizophrenia although it is associated with the cardiac arrhythmia, torsades de pointe.
Objectives: To review the effects of thioridazine for people with schizophrenia.
Search strategy: For this 2006 update, we searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's Register (June 2006).
Selection criteria: We included all randomised clinical trials comparing thioridazine with other treatments for people with schizophrenia or other psychoses.
Data collection and analysis: We reliably selected, quality rated and extracted data from relevant studies. For dichotomous data, we estimated relative risks (RR), with the 95% confidence intervals (CI). Where possible, we calculated the number needed to treat/harm statistic (NNT/H) on an intention-to-treat basis.
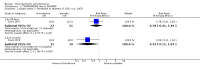
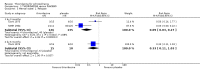
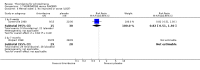
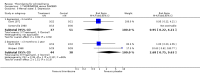
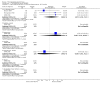
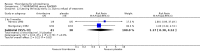
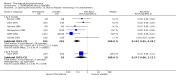
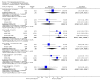
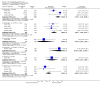
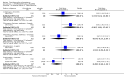
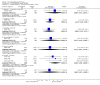
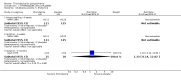
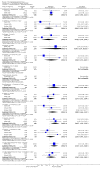
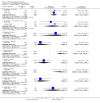
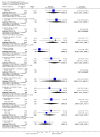
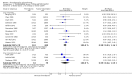
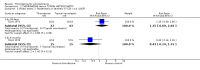
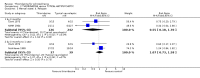
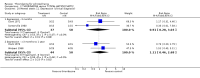
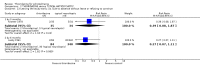
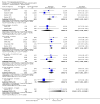
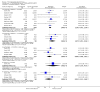
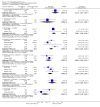
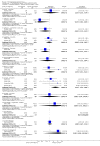
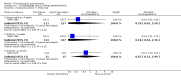
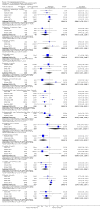
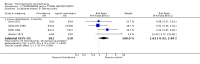
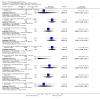
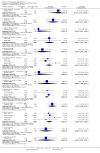
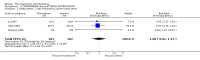
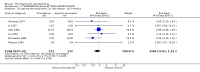
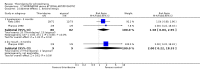
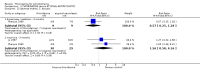
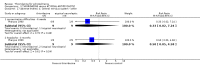
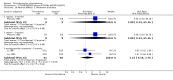
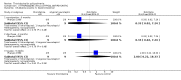
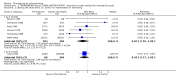
Main results: This review currently includes 42 RCTs with 3498 participants. When thioridazine was compared with placebo (total n=668, 14 RCTs) we found global state outcomes favoured thioridazine (n=105, 3 RCTs, RR 'no change or worse' by 6 months 0.33 CI 0.2 to 0.5, NNT of 2 CI 2 to 3). Thioridazine is sedating (n=324, 3 RCTs, RR 5.37 CI 3.2 to 9.1, NNH 4 CI 2 to 74). Generally, thioridazine did not cause more movement disorders than placebo.Twenty-seven studies (total n=2598) compared thioridazine with typical antipsychotics. We found no significant difference in global state (n=743, 11 RCTs, RR no short-term change or worse 0.98 CI 0.8 to 1.2) and medium-term assessments (n=142, 3 RCTs, RR 0.99, CI 0.6 to 1.6). We found no significant differences in the number of people leaving the study early 'for any reason' (short-term, n=1587, 19 RCTs, RR 1.07 CI 0.9 to 1.3). Extrapyramidal adverse events lower for those allocated to thioridazine (n=1082, 7 RCTs, RR use of antiparkinsonian drugs 0.45 CI 0.4 to 0.6). Thioridazine did seem associated with cardiac adverse effects (n=74, 1 RCT, RR 'any cardiovascular adverse event' 3.17 CI 1.4 to 7.0, NNH 3 CI 2 to 5). Electrocardiogram changes were significantly more frequent in the thioridazine group (n=254, 2 RCTs, RR 2.38, CI 1.6 to 3.6, NNH 4 CI 3 to 10). Six RCTs (total n=344) randomised thioridazine against atypical antipsychotics. Global state rating did not reveal any short-term difference between thioridazine and remoxipride and sulpiride (n=203, RR not improved or worse 1.00 CI 0.8 to 1.3). Limited data did not highlight differences in adverse event profiles.
Authors' conclusions: Although there are shortcomings, there appears to be enough consistency over different outcomes and periods to confirm that thioridazine is an antipsychotic of similar efficacy to other commonly used antipsychotics for people with schizophrenia. Its adverse events profile is similar to that of other drugs, but it may have a lower level of extrapyramidal problems and higher level of ECG changes. We would advocate the use of alternative drugs, but if its use in unavoidable, cardiac monitoring is justified.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

































Update of
-
Thioridazine for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(3):CD001944. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001944. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;(3):CD001944. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001944.pub2. PMID: 10908517 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
-
- Barker JC, Miller M. A double blind comparative trial of pericyazine and thioridazine in chronic schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1969;115(519):169‐72. - PubMed
-
- Bergling R, Mjorndal T, Oreland L, Rapp W, Wold S. Plasma levels and clinical effects of thioridazine and thiothixene. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1975;15(2‐3):178‐86. - PubMed
-
- Borison RL, Sinha D, Haverstock S, McLarnon MC, Diamond BI. Efficacy and safety of tiospirone vs. haloperidol and thioridazine in a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1989;5(2):190‐3. - PubMed
-
- Carranza Acevedo J, Angel Toro L, Gomez‐Mont F. Double blind evaluation of sulpiride and thioridazine in paranoid schizophrenia. 9th Congres de Neuropsychopharmacologie. Nouveaux Developements du Sulpiride; 1974 Jul 10, Paris. 1974. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Chen J, Zhao J, Chen Y. A randomized control study of thioridazine and chlorpromazine on treatment of schizophrenia. Chinese Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry 1995;28:329‐32.
References to studies excluded from this review
-
- Acker CW. An exploration of the autonomic effects of phenothiazines. Psychopharmacologia 1965;7(2 (Feb 15)):150‐8. - PubMed
-
- Altman H, Mehta D, Evenson RC, Sletten IW. Behavioral effects of drug therapy on psychogeriatric inpatients. I. Chlorpromazine and thioridazine. Journal of the American Geriatric Society 1973;21(6):241‐8. - PubMed
-
- Askar A, Rakhawy Y, El‐Grindy T. Thioridazine in treatment of psychiatric patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1970;211:91. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Bandelow B, Muller P, Frick U, Gaebel W, Linden M, Muller Spahn F, Pietzcker A, Tegeler J. Depressive syndromes in schizophrenic patients under neuroleptic therapy. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 1992;241(5):291‐5. - PubMed
-
- Barker JC, Miller M. A double blind comparative trial of pericyazine and thioridazine in chronic schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1969;115(519):169‐72. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
-
- Tanimukai H, Inui M, Takahashi H, Kaneko Z. A double blind comparison of sulpiride with thioridazine on schizophrenia. Seishin Igaku (Clinical Psychiatry) 1973;15(2):197‐207. [MEDLINE: ]
Additional references
-
- Annane D, Girard F, Fabre JE, Raphael JC, Gajdos P. Near fatal case of self‐poisoning with thioridazine. Intensive Care Medicine 1996 Dec;22(12):1463‐4. - PubMed
-
- Assie MB, Sleight AJ, Koek W Eur J. Biphasic displacement of [3H]YM‐09151‐2 binding in the rat brain by thioridazine, risperidone and clozapine, but not by other antipsychotics. Pharmacology 1993;237(2‐3 (Jun 24)):183‐9. - PubMed
-
- Bain TA, Healy D, Shorter E (eds). The rise of psychopharmacology and the story of CINP. Budapest: Animula Publishing House, 1998.
-
- Begg C, Cho M, Eastwood S, Horton R, Moher D, Olkin I, Pitkin R, Rennie D, Schulz KF, Simel D, Stroup DF. Improving the quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials: the CONSORT statement. JAMA 1996;276(8):637‐9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

