Heritability of susceptibility to ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis of human lymphocyte subpopulations
- PMID: 17637392
- PMCID: PMC1994900
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.03.050
Heritability of susceptibility to ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis of human lymphocyte subpopulations
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the heritability of intrinsic radiosensitivity, the induction of apoptosis in lymphocyte subpopulations was determined on samples from related individuals belonging to large kindred families.
Methods and materials: Quiescent lymphocytes from 334 healthy individuals were gamma-irradiated in vitro. Apoptosis was determined 18 h after irradiation by eight-color flow cytometry. Radiosensitivity was quantified from dose-effect curves. Intrafamilial correlations and heritability were computed for 199 father-mother-offspring trios using the programs SOLAR (Sequential Oligogenic Linkage Analysis Routines) and SAGE (Statistical Analysis for Genetic Epidemiology). Segregation analyses were conducted using SAGE.
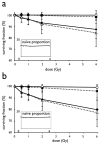
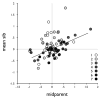
Results: Marked differential susceptibility of naive and memory T lymphocytes was demonstrated. Also, although age and gender were significant covariates, their effects only accounted for a minor part of the inter-individual variation. Parent-offspring and sib-sib correlations were significant for the radiosensitivity of B cells, T4, and T8 and of effector memory T4 and T8 subpopulations. In the T4-effector memory subpopulation, the phenotype showed correlations most consistent with dominant or additive genetic effects, and the results of the segregation analysis were consistent with the contribution of a bi-allelic dominant locus.
Conclusions: Heritability was demonstrated for the susceptibility to ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis of lymphocyte populations, and the segregation of the T4-effector memory radiosensitivity phenotype was consistent with a simple mendelian transmission model involving one major gene.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intrinsic susceptibility to radiation-induced apoptosis of human lymphocyte subpopulations.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003 Nov 1;57(3):769-78. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00637-0. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. PMID: 14529783
-
Rapid assay of intrinsic radiosensitivity based on apoptosis in human CD4 and CD8 T-lymphocytes.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997 May 1;38(2):429-40. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(97)00038-2. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997. PMID: 9226332
-
TNFSF10/TRAIL regulates human T4 effector memory lymphocyte radiosensitivity and predicts radiation-induced acute and subacute dermatitis.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 19;7(16):21416-27. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7893. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26982083 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the ratio of CD4+ to CD8+ T-cells on radiation-induced apoptosis in human lymphocyte subpopulations.Int J Radiat Biol. 2002 Aug;78(8):681-8. doi: 10.1080/09553000210144475. Int J Radiat Biol. 2002. PMID: 12194751
-
Radiation-induced lymphocyte apoptosis to predict radiation therapy late toxicity in prostate cancer patients.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009 Aug 1;74(5):1424-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.10.039. Epub 2009 Jan 23. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009. PMID: 19167839
Cited by
-
Senescence-like Phenotype After Chronic Exposure to Isoproterenol in Primary Quiescent Immune Cells.Biomolecules. 2024 Nov 28;14(12):1528. doi: 10.3390/biom14121528. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766235 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic determinants of neuronal vulnerability to apoptosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Jan;70(1):71-88. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1029-y. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22695677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Normal tissue reactions to radiotherapy: towards tailoring treatment dose by genotype.Nat Rev Cancer. 2009 Feb;9(2):134-42. doi: 10.1038/nrc2587. Epub 2009 Jan 16. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19148183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telomere Length Dynamics and Chromosomal Instability for Predicting Individual Radiosensitivity and Risk via Machine Learning.J Pers Med. 2021 Mar 8;11(3):188. doi: 10.3390/jpm11030188. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33800260 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Germline Genetics in Identifying Survivors at Risk for Adverse Effects of Cancer Treatment.Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2018 May 23;38(38):775-786. doi: 10.1200/EDBK_201391. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2018. PMID: 30231410 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parshad R, Sanford KK. Radiation-induced chromatid breaks and deficient DNA repair in cancer predisposition. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2001;37:87–96. - PubMed
-
- German J, Ellis NA. Bloom syndrome. In: Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW, editors. The genetic basis of human cancer. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2002. pp. 267–288.
-
- Varga D, Hoegel J, Maier C, et al. On the difference of micronucleus frequencies in peripheral blood lymphocytes between breast cancer patients and controls. Mutagenesis. 2006;21:313–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

