A bacterial E3 ubiquitin ligase targets a host protein kinase to disrupt plant immunity
- PMID: 17637671
- PMCID: PMC2265072
- DOI: 10.1038/nature05966
A bacterial E3 ubiquitin ligase targets a host protein kinase to disrupt plant immunity
Abstract
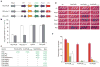
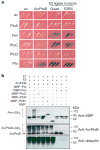
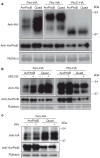
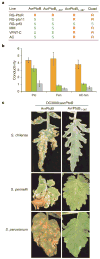
Many bacterial pathogens of plants and animals use a type III secretion system to deliver diverse virulence-associated 'effector' proteins into the host cell. The mechanisms by which these effectors act are mostly unknown; however, they often promote disease by suppressing host immunity. One type III effector, AvrPtoB, expressed by the plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato, has a carboxy-terminal domain that is an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Deletion of this domain allows an amino-terminal region of AvrPtoB (AvrPtoB(1-387)) to be detected by certain tomato varieties leading to immunity-associated programmed cell death. Here we show that a host kinase, Fen, physically interacts with AvrPtoB(1-387 )and is responsible for activating the plant immune response. The AvrPtoB E3 ligase specifically ubiquitinates Fen and promotes its degradation in a proteasome-dependent manner. This degradation leads to disease susceptibility in Fen-expressing tomato lines. Various wild species of tomato were found to exhibit immunity in response to AvrPtoB(1-387 )and not to full-length AvrPtoB. Thus, by acquiring an E3 ligase domain, AvrPtoB has thwarted a highly conserved host resistance mechanism.
Figures
References
-
- Mudgett MB. New insights to the function of phytopathogenic bacterial type III effectors in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2005;56:509–531. - PubMed
-
- Janjusevic R, Abramovitch RB, Martin GB, Stebbins CE. A bacterial inhibitor of host programmed cell death defenses is an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Science. 2006;311:222–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

