The neuro-steroid, 3beta androstene 17alpha diol exhibits potent cytotoxic effects on human malignant glioma and lymphoma cells through different programmed cell death pathways
- PMID: 17637679
- PMCID: PMC2360358
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603894
The neuro-steroid, 3beta androstene 17alpha diol exhibits potent cytotoxic effects on human malignant glioma and lymphoma cells through different programmed cell death pathways
Abstract
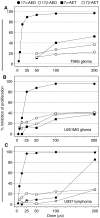
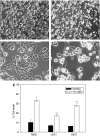
The neuro-steroids 3beta-androstene-17alpha-diol (17alpha-AED), 3beta-androstene-17beta-diol (17beta-AED), 3beta-androstene-7alpha,-17beta-triol (7alpha-AET) and 3beta-androstene-7beta,-17beta-triol (7beta-AET) are metabolites of dehydroepiandrosterone and are produced in neuro-ectodermal tissue. Both epimers of androstenediols (17alpha-AED and 17beta-AED) and androstenetriols (7alpha-AET and 7beta-AET) have markedly different biological functions of their chemical analogue. We investigated the cytotoxic activity of these neuro-steroids on human T98G and U251MG glioblastoma and U937 lymphoma cells. Proliferation studies showed that 17alpha-AED is the most potent inhibitor, with an IC(50) approximately 15 microM. For T98G glioma, 90% inhibition was achieved with 25 muM of 17alpha-AED. Other neuro-steroids tested only marginally suppressed cell proliferation. Reduced cell adherence and viability could be detected after 18 h of 17alpha-AED exposure. Treatment with 17alpha-AED induced a significant level of apoptosis in U937 lymphoma cells, but not in the glioma cells. Cytopathology of 17alpha-AED-treated T98G cells revealed the presence of multiple cytoplasmic vacuoles. Acridine orange staining demonstrated the formation of acidic vesicular organelles in 17alpha-AED-treated T98G and U251MG, which was inhibited by bafilomycin A1. These findings indicate that 17alpha-AED bears the most potent cytotoxic activity of the neuro-steroids tested, and the effectiveness may depend on the number of hydroxyls and their position on the androstene molecule. These cytotoxic effects may utilize a non-apoptotic pathway in malignant glioma cells.
Figures



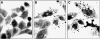

Similar articles
-
The anti-tumor effects of androstene steroids exhibit a strict structure-activity relationship dependent upon the orientation of the hydroxyl group on carbon-17.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2009 Dec;74(6):625-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2009.00900.x. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2009. PMID: 19824892
-
Autophagy and the functional roles of Atg5 and beclin-1 in the anti-tumor effects of 3beta androstene 17alpha diol neuro-steroid on malignant glioma cells.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2009 Jul;115(3-5):137-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2009.03.013. Epub 2009 Apr 16. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19375507
-
The neuro-steroid, 5-androstene 3β,17α diol; induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy through PERK/eIF2α signaling in malignant glioma cells and transformed fibroblasts.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;42(12):2019-29. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.09.003. Epub 2010 Sep 18. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20851775
-
17α-androstenediol-mediated oncophagy of tumor cells by different mechanisms is determined by the target tumor.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Jul;1262:127-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06602.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 22823444 Review.
-
Galanin suppresses proliferation of human U251 and T98G glioma cells via its subtype 1 receptor.Biol Chem. 2017 Sep 26;398(10):1127-1139. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2016-0320. Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28525358 Review.
Cited by
-
New 6,19-oxidoandrostan derivatives obtained by biotransformation in environmental filamentous fungi cultures.Microb Cell Fact. 2020 Feb 17;19(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01303-6. Microb Cell Fact. 2020. PMID: 32066453 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Effect of Wortmannolone Derivatives on MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells.Anticancer Res. 2017 Apr;37(4):1617-1623. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11492. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28373422 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydroepiandrosterone and Its Metabolite 5-Androstenediol: New Therapeutic Targets and Possibilities for Clinical Application.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 9;17(9):1186. doi: 10.3390/ph17091186. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isoforms of autophagy-related proteins: role in glioma progression and therapy resistance.Mol Cell Biochem. 2022 Feb;477(2):593-604. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04308-w. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 34854022 Review.
-
Structural Stereochemistry of Androstene Hormones Determines Interactions with Human Androgen, Estrogen, and Glucocorticoid Receptors.Int J Med Chem. 2013 Mar 14;2013:203606. doi: 10.1155/2013/203606. Int J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24729874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ben Nathan D, Padgett DA, Loria RM (1999) Androstenediol and dehydroepiandrosterone protect mice against lethal bacterial infections and lipopolysaccharide toxicity. J Med Microbiol 48: 425–431 - PubMed
-
- Boccuzzi G, Di Monaco M, Brignardello E, Leonardi L, Gatto V, Pizzini A, Gallo M (1993) Dehydroepiandrosterone antiestrogenic action through androgen receptor in MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. Anticancer Res 13: 2267–2272 - PubMed
-
- Bursch W, Ellinger A, Gerner C, Frohwein U, Schulte-Hermann R (2000) Programmed cell death (PCD). Apoptosis, autophagic PCD, or others? Ann N Y Acad Sci 926: 1–12 - PubMed
-
- Huynh PN, Carter Jr WH, Loria RM (2000) 17 Alpha androstenediol inhibition of breast tumor cell proliferation in estrogen receptor-positive and -negative cell lines. Cancer Detect Prev 24: 435–444 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

