Blood metallothionein transcript as a biomarker for metal sensitivity: low blood metallothionein transcripts in arsenicosis patients from Guizhou, China
- PMID: 17637929
- PMCID: PMC1913577
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.10035
Blood metallothionein transcript as a biomarker for metal sensitivity: low blood metallothionein transcripts in arsenicosis patients from Guizhou, China
Abstract
Background: Because metallothionein (MT) is a metal-binding protein that protects against metal intoxication, it could be a biomarker for individual sensitivity to metal toxicity.
Objective: We assessed the use of bloodborne MT transcript as a reflection of tissue MT levels and examined the potential role of MT in arsenic toxicity in an environmentally exposed human population.
Method: Rodents were treated with zinc or nonmetallic MT inducers for 4 days, and the blood and tissues were collected for MT transcript analysis by real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and MT protein determination by the cadmium-hemoglobin assay. Blood and buccal cell samples were collected from arsenicosis patients and healthy subjects residing in Guizhou, China, and total RNA was isolated for MT transcript analysis.
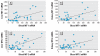
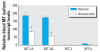
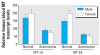
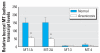
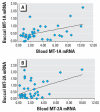
Results: There was a positive correlation between blood MT-1 and MT-2 transcripts and corresponding hepatic or renal MT transcript levels in rats and mice. Furthermore, there was a positive correlation between blood MT-1 and MT-2 transcript and tissue MT protein levels in these animals. A positive correlation also occurred between human blood MT and buccal cell MT transcript levels. MT-1A and MT-2A were the major isoform transcripts in human blood and buccal cells, and significantly lower MT levels were seen in arsenicosis patients compared with healthy subjects.
Conclusions: Blood MT transcript appears to be a useful biomarker of tissue MT levels. Arsenicosis patients in Guizhou show significantly lower MT transcript levels in blood, which may have predisposed this population to arsenic intoxication.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression and regulation of metallothionein mRNA levels in the prostates of noble rats: lack of expression in the ventral prostate and regulation by sex hormones in the dorsolateral prostate.Prostate. 1996 Aug;29(2):91-100. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0045(199608)29:2<91::AID-PROS4>3.0.CO;2-K. Prostate. 1996. PMID: 8700805
-
Differential regulation of the two metallothionein genes in common carp.Acta Biol Hung. 2002;53(3):343-50. doi: 10.1556/ABiol.53.2002.3.11. Acta Biol Hung. 2002. PMID: 12371614
-
[Study on blood and buccal mucous related genes expression in the patients suffering from coal-burning arsenism].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009 Jun 2;89(21):1446-9. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19953893 Chinese.
-
Metallothionein gene and protein expression as a biomarker for metal pollution in natural gudgeon populations.Aquat Toxicol. 2007 May 15;82(3):163-72. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.02.008. Epub 2007 Feb 20. Aquat Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17379326
-
Metallothionein Lower Under-Expression in Benign Tumors than That in Malignant Tumors: Systematic Review Article and Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2014 Jun;43(6):696-704. Iran J Public Health. 2014. PMID: 26110140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of cadmium chloride on metallothionein levels in carp.Sensors (Basel). 2009;9(6):4789-803. doi: 10.3390/s90604789. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Sensors (Basel). 2009. PMID: 22408554 Free PMC article.
-
Early life inorganic lead exposure induces testicular teratoma and renal and urinary bladder preneoplasia in adult metallothionein-knockout mice but not in wild type mice.Toxicology. 2010 Sep 30;276(1):5-10. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2010.06.006. Epub 2010 Jun 23. Toxicology. 2010. PMID: 20600549 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide donor, V-PROLI/NO, provides protection against arsenical induced toxicity in rat liver cells: requirement for Cyp1a1.Chem Biol Interact. 2011 Aug 15;193(1):88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2011.05.005. Epub 2011 May 20. Chem Biol Interact. 2011. PMID: 21621526 Free PMC article.
-
The nitric oxide prodrug, V-PYRRO/NO, mitigates arsenic-induced liver cell toxicity and apoptosis.Cancer Lett. 2007 Oct 28;256(2):238-45. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2007.06.009. Epub 2007 Jul 20. Cancer Lett. 2007. PMID: 17658681 Free PMC article.
-
Metallothionein blocks oxidative DNA damage induced by acute inorganic arsenic exposure.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015 Feb 1;282(3):267-74. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2014.11.014. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25485709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad SA, Sayed MH, Faruquee MH, Khan MH, Jalil MA, Ahmed R, et al. Arsenicosis: sex differentials. J Prev Soc Med. 1999;18:35–40. - PubMed
-
- Albores A, Koropatnick J, Cherian MG, Zelazowski AJ. Arsenic induces and enhances rat hepatic metallothionein production in vivo. Chem-Biol Interact. 1992;85:127–140. - PubMed
-
- Allan AK, Hawksworth GM, Woodhouse LR, Sutherland B, King JC, Beattie JH. Lymphocyte metallothionein mRNA responds to marginal zinc intake in human volunteers. Br J Nutr. 2000;84:747–756. - PubMed
-
- Bem EM, Piotrowski JK, Sobczak-Kozlowska M, Dmuchowski C. Cadmium, zinc, copper and metallothionein levels in human liver. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1988;60:413–417. - PubMed
-
- Chang XL, Jin TY, Zhou YF. Metallothionein 1 isoform gene expression induced by cadmium in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Biomed Environ Sci. 2006;19:104–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

