Interferon-alpha promotes abnormal vasculogenesis in lupus: a potential pathway for premature atherosclerosis
- PMID: 17638846
- PMCID: PMC2018671
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-089086
Interferon-alpha promotes abnormal vasculogenesis in lupus: a potential pathway for premature atherosclerosis
Abstract
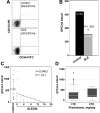
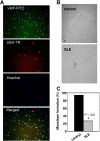
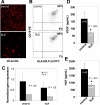
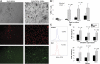
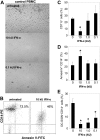
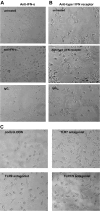
Individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have a striking increase in premature atherosclerosis of unclear etiology. Accelerated endothelial cell apoptosis occurs in SLE and correlates with endothelial dysfunction. Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and myelomonocytic circulating angiogenic cells (CACs) are crucial in blood vessel repair after vascular damage, and decreased levels or abnormal function of EPCs/CACs are established atherosclerosis risk factors. We investigated if vascular repair is impaired in SLE. We report that SLE patients display abnormal phenotype and function of EPCs/CACs. These abnormalities are characterized by significant decreases in the number of circulating EPCs (310 +/- 50 EPCs/mL of blood in SLE versus 639 +/- 102 in controls) and significant impairments in the capacity of EPCs/CACs to differentiate into mature ECs and synthesize adequate levels of the proangiogenic molecules vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hepatic growth factor (HGF). These abnormalities are triggered by interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha), which induces EPC and CAC apoptosis and skews myeloid cells toward nonangiogenic phenotypes. Lupus EPCs/CACs have increased IFN-alpha expression and their supernatants promote higher induction of IFN-inducible genes. Importantly, neutralization of IFN pathways restores a normal EPC/CAC phenotype in lupus. SLE is characterized by an imbalance between endothelial cell damage and repair triggered by type I IFNs, which might promote accelerated atherosclerosis.
Figures
References
-
- Ward MM. Premature morbidity from cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:338–346. - PubMed
-
- Esdaile JM, Abrahamowicz M, Grodzicky T, et al. Traditional Framingham risk factors fail to fully account for accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:2331–2337. - PubMed
-
- Rajagopalan S, Somers EC, Brook RD, et al. Endothelial cell apoptosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: a common pathway for abnormal vascular function and thrombosis propensity. Blood. 2004;103:3677–3683. - PubMed
-
- Choy JC, Granville DJ, Hunt DW, McManus BM. Endothelial cell apoptosis: biochemical characteristics and potential implications for atherosclerosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001;33:1673–1690. - PubMed
-
- Luttun A, Carmeliet G, Carmeliet P. Vascular progenitors: from biology to treatment. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2002;12:88–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

