The multifunctional protein p54nrb/PSF recruits the exonuclease XRN2 to facilitate pre-mRNA 3' processing and transcription termination
- PMID: 17639083
- PMCID: PMC1920172
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1565207
The multifunctional protein p54nrb/PSF recruits the exonuclease XRN2 to facilitate pre-mRNA 3' processing and transcription termination
Abstract
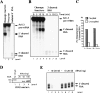
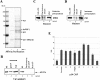
Termination of RNA polymerase II transcription frequently requires a poly(A) signal and cleavage/polyadenylation factors. Recent work has shown that degradation of the downstream cleaved RNA by the exonuclease XRN2 promotes termination, but how XRN2 functions with 3'-processing factors to elicit termination remains unclear. Here we show that XRN2 physically associates with 3'-processing factors and accumulates at the 3' end of a transcribed gene. In vitro 3'-processing assays show that XRN2 is necessary to degrade the downstream RNA, but is not required for 3' cleavage. Significantly, degradation of the 3'-cleaved RNA was stimulated when coupled to cleavage. Unexpectedly, while investigating how XRN2 is recruited to the 3'-processing machinery, we found that XRN2 associates with p54nrb/NonO(p54)-protein-associated splicing factor (PSF), multifunctional proteins involved in several nuclear processes. Strikingly, p54 is also required for degradation of the 3'-cleaved RNA in vitro. p54 is present along the length of genes, and small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated knockdown leads to defects in XRN2 recruitment and termination. Together, our data indicate that p54nrb/PSF functions in recruitment of XRN2 to facilitate pre-mRNA 3' processing and transcription termination.
Figures
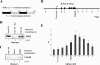




References
-
- Ahn S.H., Kim M., Buratowski S., Kim M., Buratowski S., Buratowski S. Phosphorylation of serine 2 within the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain couples transcription and 3′ end processing. Mol. Cell. 2004;13:67–76. - PubMed
-
- Bashkirov V.I., Scherthan H., Solinger J.A., Buerstedde J.M., Heyer W.D., Scherthan H., Solinger J.A., Buerstedde J.M., Heyer W.D., Solinger J.A., Buerstedde J.M., Heyer W.D., Buerstedde J.M., Heyer W.D., Heyer W.D. A mouse cytoplasmic exoribonuclease (mXRN1p) with preference for G4 tetraplex substrates. J. Cell Biol. 1997;136:761–773. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birse C.E., Minvielle-Sebastia L., Lee B.A., Keller W., Proudfoot N.J., Minvielle-Sebastia L., Lee B.A., Keller W., Proudfoot N.J., Lee B.A., Keller W., Proudfoot N.J., Keller W., Proudfoot N.J., Proudfoot N.J. Coupling termination of transcription to messenger RNA maturation in yeast. Science. 1998;280:298–301. - PubMed
-
- Bousquet-Antonelli C., Presutti C., Tollervey D., Presutti C., Tollervey D., Tollervey D. Identification of a regulated pathway for nuclear pre-mRNA turnover. Cell. 2000;102:765–775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
