Palytoxin acts on Na(+),K (+)-ATPase but not nongastric H(+),K (+)-ATPase
- PMID: 17639367
- PMCID: PMC2396460
- DOI: 10.1007/s00232-007-9040-1
Palytoxin acts on Na(+),K (+)-ATPase but not nongastric H(+),K (+)-ATPase
Abstract
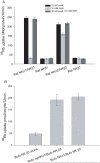
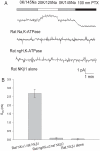
Palytoxin (PTX) opens a pathway for ions to pass through Na,K-ATPase. We investigate here whether PTX also acts on nongastric H,K-ATPases. The following combinations of cRNA were expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes: Bufo marinus bladder H,K-ATPase alpha(2)- and Na,K-ATPase beta(2)-subunits; Bufo Na,K-ATPase alpha(1)- and Na,K-ATPase beta(2)-subunits; and Bufo Na,K-ATPase beta(2)-subunit alone. The response to PTX was measured after blocking endogenous Xenopus Na,K-ATPase with 10 microM ouabain. Functional expression was confirmed by measuring (86)Rb uptake. PTX (5 nM: ) produced a large increase of membrane conductance in oocytes expressing Bufo Na,K-ATPase, but no significant increase occurred in oocytes expressing Bufo H,K-ATPase or in those injected with Bufo beta(2)-subunit alone. Expression of the following combinations of cDNA was investigated in HeLa cells: rat colonic H,K-ATPase alpha(1)-subunit and Na,K-ATPase beta(1)-subunit; rat Na,K-ATPase alpha(2)-subunit and Na,K-ATPase beta(2)-subunit; and rat Na,K-ATPase beta(1)- or Na,K-ATPase beta(2)-subunit alone. Measurement of increases in (86)Rb uptake confirmed that both rat Na,K and H,K pumps were functional in HeLa cells expressing rat colonic HKalpha(1)/NKbeta(1) and NKalpha(2)/NKbeta(2). Whole-cell patch-clamp measurements in HeLa cells expressing rat colonic HKalpha(1)/NKbeta(1) exposed to 100 nM PTX showed no significant increase of membrane current, and there was no membrane conductance increase in HeLa cells transfected with rat NKbeta(1)- or rat NKbeta(2)-subunit alone. However, in HeLa cells expressing rat NKalpha(2)/NKbeta(2), outward current was observed after pump activation by 20 mM K(+) and a large membrane conductance increase occurred after 100 nM PTX. We conclude that nongastric H,K-ATPases are not sensitive to PTX when expressed in these cells, whereas PTX does act on Na,K-ATPase.
Figures

References
-
- Burnay M, Crambert G, Geering K, Horisberger J-D. Bufo marinus bladder H-K-ATPase carries out electroneutral ion transport. Am. J. Physiol. 2001;281:F869–F874. - PubMed
-
- Caplan MJ. Ion pumps in epithelial cells: sorting, stabilization, and polarity. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:G1304–G1313. - PubMed
-
- Cantley LG, Resh MD, Guidoti G. Vanadate Inhibits the red cell Na,K-ATPase from the cytoplasmic side. Nature. 1978;272:552–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

