Protein abundance ratios for global studies of prokaryotes
- PMID: 17639608
- PMCID: PMC2660852
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.200700267
Protein abundance ratios for global studies of prokaryotes
Abstract
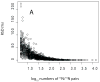
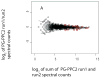
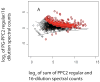
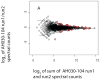
The use of multidimensional capillary HPLC combined with MS/MS has allowed high qualitative and quantitative proteome coverage of prokaryotic organisms. The determination of protein abundance change between two or more conditions has matured to the point that false discovery rates can be very low and for smaller proteomes coverage is sufficiently high to explicitly consider false negative error. Selected aspects of using these methods for global protein abundance assessments are reviewed. These include instrumental issues that influence the reliability of abundance ratios; a comparison of sources of nonlinearity, errors, and data compression in proteomics and spotted cDNA arrays; strengths and weaknesses of spectral counting versus stable isotope metabolic labeling; and a survey of microbiological applications of global abundance analysis at the protein level. Proteomic results for two organisms that have been studied extensively using these methods are reviewed in greater detail. Spectral counting and metabolic labeling data are compared and the utility of proteomics for global gene regulation studies are discussed for the methanogenic Archaeon Methanococcus maripaludis. The oral pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis is discussed as an example of an organism where a large percentage of the proteome differs in relative abundance between the intracellular and extracellular phenotype.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Quantitative proteomics of intracellular Porphyromonas gingivalis.Proteomics. 2007 Dec;7(23):4323-37. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200700543. Proteomics. 2007. PMID: 17979175 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of spectral counting and metabolic stable isotope labeling for use with quantitative microbial proteomics.Analyst. 2006 Dec;131(12):1335-41. doi: 10.1039/b610957h. Epub 2006 Oct 11. Analyst. 2006. PMID: 17124542 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics and its application to studies of Porphyromonas gingivalis invasion and pathogenicity.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2006 Sep;6(3):311-25. doi: 10.2174/187152606778249935. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16918489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative proteomics of the archaeon Methanococcus maripaludis validated by microarray analysis and real time PCR.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006 May;5(5):868-81. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M500369-MCP200. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006. PMID: 16489187 Free PMC article.
-
[Applications of high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in proteomics].Se Pu. 2024 Jul;42(7):601-612. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2023.11006. Se Pu. 2024. PMID: 38966969 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive proteomics of Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 metabolism under single carbon and nonmethylotrophic conditions.Proteomics. 2008 Sep;8(17):3494-505. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200800152. Proteomics. 2008. PMID: 18686303 Free PMC article.
-
Effective correction of experimental errors in quantitative proteomics using stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC).J Proteomics. 2012 Jun 27;75(12):3720-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2012.04.035. Epub 2012 May 7. J Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22575385 Free PMC article.
-
Pathway analysis for intracellular Porphyromonas gingivalis using a strain ATCC 33277 specific database.BMC Microbiol. 2009 Sep 1;9:185. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-185. BMC Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19723305 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics of Porphyromonas gingivalis within a model oral microbial community.BMC Microbiol. 2009 May 19;9:98. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-98. BMC Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19454014 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic identification of novel proteins associated with Lewy bodies.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:3850-6. doi: 10.2741/2973. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ishii N, Robert M, Nakayama Y, Kanai A, Tomita M. Toward large-scale modeling of the microbial cell for computer simulation. J Biotechnol. 2004;113:281–294. - PubMed
-
- Souchelnytskyi S. Bridging proteomics and systems biology: what are the roads to be traveled? Proteomics. 2005;5:4123–4137. - PubMed
-
- Mayya V, Han KD. Proteomic applications of protein quantification by isotope-dilution mass spectrometry. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2006;3:597–610. - PubMed
-
- Domon B, Aebersold R. Mass spectrometry and protein analysis. Science. 2006;312:212–217. - PubMed
-
- Quackenbush J. Animal Genet. 37 Suppl 1. 2006. From’omes to biology; pp. 48–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

