MIF coordinates the cell cycle with DNA damage checkpoints. Lessons from knockout mouse models
- PMID: 17640378
- PMCID: PMC1941730
- DOI: 10.1186/1747-1028-2-22
MIF coordinates the cell cycle with DNA damage checkpoints. Lessons from knockout mouse models
Abstract
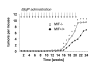
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is a ubiquitously expressed pro-inflammatory mediator that has also been implicated in the process of oncogenic transformation and tumor progression. We used a genetic approach to show that deletion of the MIF gene in mice has several major consequences for the proliferative and transforming properties of cells. MIF-deficient cells exhibit increased resistance to oncogenic transformation. The transformation defects associated with MIF deficiency can be overcome through concomitant inactivation of the p53 and Rb/E2F tumor suppressor pathways. We have produced compelling evidence that the effects of MIF on cell survival and tumorigenesis are mediated through overlapping pathways, wherein MIF and p53 functionally antagonize each other in the cell. However, the involvement of MIF in p53 function is secondary to p53-independent mechanisms controlling protein stability, DNA damage checkpoints, and the integrity of the genome. Given the broad spectrum of cell types that normally express MIF and its elevated levels at sites of chronic inflammation, this pathway may be generic for many early stage tumors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor MIF interferes with the Rb-E2F pathway.Mol Cell. 2005 Jan 21;17(2):225-36. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.11.052. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15664192
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor deficiency is associated with altered cell growth and reduced susceptibility to Ras-mediated transformation.J Biol Chem. 2003 Mar 28;278(13):11078-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211985200. Epub 2003 Jan 21. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12538581
-
The p53-dependent effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor revealed by gene targeting.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Aug 5;100(16):9354-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1533295100. Epub 2003 Jul 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12878730 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor coordinates DNA damage response with the proteasomal control of the cell cycle.Cell Cycle. 2007 May 2;6(9):1030-4. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.9.4163. Epub 2007 May 20. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17426455 Review.
-
New therapeutic target in inflammatory disease: macrophage migration inhibitory factor.Intern Med J. 2005 Jul;35(7):419-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.2005.00853.x. Intern Med J. 2005. PMID: 15958113 Review.
Cited by
-
A tautomerase-null macrophage migration-inhibitory factor (MIF) gene knock-in mouse model reveals that protein interactions and not enzymatic activity mediate MIF-dependent growth regulation.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;29(7):1922-32. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01907-08. Epub 2009 Feb 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19188446 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor deficiency in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 Mar 15;306(6):L487-96. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00284.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24441872 Free PMC article.
-
A predicted protein, KIAA0247, is a cell cycle modulator in colorectal cancer cells under 5-FU treatment.J Transl Med. 2011 May 28;9:82. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-82. J Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21619678 Free PMC article.
-
Role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in age-related lung disease.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 Jul 1;309(1):L1-10. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00339.2014. Epub 2015 May 8. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25957294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial CD74 mediates macrophage migration inhibitory factor protection in hyperoxic lung injury.FASEB J. 2015 May;29(5):1940-9. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-260299. Epub 2015 Jan 21. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25609432 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

