Cryptic animal species are homogeneously distributed among taxa and biogeographical regions
- PMID: 17640383
- PMCID: PMC1939701
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-121
Cryptic animal species are homogeneously distributed among taxa and biogeographical regions
Abstract
Background: Cryptic species are two or more distinct but morphologically similar species that were classified as a single species. During the past two decades we observed an exponential growth of publications on cryptic species. Recently published reviews have demonstrated cryptic species have profound consequences on many biological disciplines. It has been proposed that their distribution is non-random across taxa and biomes.
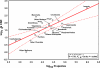
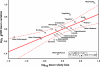
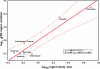
Results: We analysed a literature database for the taxonomic and biogeographical distribution of cryptic animal species reports. Results from regression analysis indicate that cryptic species are almost evenly distributed among major metazoan taxa and biogeographical regions when corrected for species richness and study intensity.
Conclusion: This indicates that morphological stasis represents an evolutionary constant and that cryptic metazoan diversity does predictably affect estimates of earth's animal diversity. Our findings have direct theoretical and practical consequences for a number of prevailing biological questions with regard to global biodiversity estimates, conservation efforts and global taxonomic initiatives.
Figures

References
-
- Consortium for the Barcode of Life Consortium for the Barcode of Life: A global standard for identifying biological species http://barcoding.si.edu/
-
- Baillie JEM, Hilton-Taylor C, Stuart SN. 2004 IUCN Red List of threatened species. A global species assessment. Gland and Cambridge , The IUCN Species Survival Commision; 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

