Search for allosteric disulfide bonds in NMR structures
- PMID: 17640393
- PMCID: PMC1949407
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6807-7-49
Search for allosteric disulfide bonds in NMR structures
Abstract
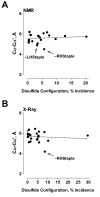
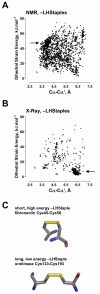
Background: Allosteric disulfide bonds regulate protein function when they break and/or form. They typically have a -RHStaple configuration, which is defined by the sign of the five chi angles that make up the disulfide bond.
Results: All disulfides in NMR and X-ray protein structures as well as in refined structure datasets were compared and contrasted for configuration and strain energy.
Conclusion: The mean dihedral strain energy of 55,005 NMR structure disulfides was twice that of 42,690 X-ray structure disulfides. Moreover, the energies of all twenty types of disulfide bond was higher in NMR structures than X-ray structures, where there was an exponential decrease in the mean strain energy as the incidence of the disulfide type increased. Evaluation of protein structures for which there are X-ray and NMR models shows that the same disulfide bond can exist in different configurations in different models. A disulfide bond configuration that is rare in X-ray structures is the -LHStaple. In NMR structures, this disulfide is characterised by a particularly high potential energy and very short alpha-carbon distance. The HIV envelope glycoprotein gp120, for example, is regulated by thiol/disulfide exchange and contains allosteric -RHStaple bonds that can exist in the -LHStaple configuration. It is an open question which form of the disulfide is the functional configuration.
Figures

References
-
- Brooks DJ, Fresco JR, Lesk AM, Singh M. Evolution of amino acid frequencies in proteins over deep time: inferred order of introduction of amino acids into the genetic code. Mol Biol Evol. 2002;19:1645–1655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

