Regulatory mechanisms to control tissue alpha-tocopherol
- PMID: 17640571
- PMCID: PMC2693716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.05.027
Regulatory mechanisms to control tissue alpha-tocopherol
Abstract
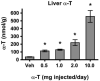
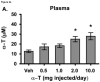
To test the hypothesis that hepatic regulation of alpha-tocopherol metabolism would be sufficient to prevent overaccumulation of alpha-tocopherol in extrahepatic tissues and that administration of high doses of alpha-tocopherol would up-regulate extrahepatic xenobiotic pathways, rats received daily subcutaneous injections of either vehicle or 0.5, 1, 2, or 10 mg alpha-tocopherol/100 g body wt for 9 days. Liver alpha-tocopherol increased 15-fold in rats given 10 mg alpha-tocopherol/100 g body wt (mg/100 g) compared with controls. Hepatic alpha-tocopherol metabolites increased with increasing alpha-tocopherol doses, reaching 40-fold in rats given the highest dose. In rats injected with 10 mg/100 g, lung and duodenum alpha-tocopherol concentrations increased 3-fold, whereas alpha-tocopherol concentrations of other extrahepatic tissues increased 2-fold or less. With the exception of muscle, daily administration of less than 2 mg/100 g failed to increase alpha-tocopherol concentrations in extrahepatic tissues. Lung cytochrome P450 3A and 1A levels were unchanged by administration of alpha-tocopherol at any dose. In contrast, lung P-glycoprotein (MDR1) levels increased dose dependently and expression of this xenobiotic transport protein was correlated with lung alpha-tocopherol concentrations (R(2)=0.88, p<0.05). Increased lung MDR1 may provide protection from exposure to environmental toxins by increasing alveolar space alpha-tocopherol.
Figures



















References
-
- Traber MG, Burton GW, Hamilton RL. Vitamin E trafficking. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2005;1031:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Schultz M, Leist M, Petrzika M, Gassmann B, Brigelius-Flohé R. Novel urinary metabolite of alpha-tocopherol, 2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2(2′-carboxyethyl)-6-hydroxychroman, as an indicator of an adequate vitamin E supply? Am J Clin Nutr. 1995;62(suppl):1527S–1534S. - PubMed
-
- Sontag TJ, Parker RS. Cytochrome P450 omega-hydroxylase pathway of tocopherol catabolism: Novel mechanism of regulation of vitamin E status. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:25290–25296. - PubMed
-
- Mustacich DJ, Leonard SW, Devereaux MW, Sokol RJ, Traber MG. α-Tocopherol regulation of hepatic cytochrome P450s and ABC transporters in rats. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;41:1069–1078. - PubMed
-
- Traber MG, Siddens LK, Leonard SW, Schock B, Gohil K, Krueger SK, Cross CE, Williams DE. α-Tocopherol modulates Cyp3a expression, increases γ-CEHC production and limits tissue γ-tocopherol accumulation in mice fed high γ-tocopherol diets. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005;38:773–785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

