Genomic analysis of CD8+ NK/T cell line, 'SRIK-NKL', with array-based CGH (aCGH), SKY/FISH and molecular mapping
- PMID: 17640729
- PMCID: PMC2855542
- DOI: 10.1016/j.leukres.2007.04.019
Genomic analysis of CD8+ NK/T cell line, 'SRIK-NKL', with array-based CGH (aCGH), SKY/FISH and molecular mapping
Abstract
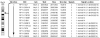
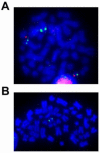
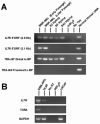
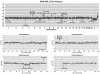
We performed aCGH, SKY/FISH, molecular mapping and expression analyses on a permanent CD8+ NK/T cell line, 'SRIK-NKL' established from a lymphoma (ALL) patient, in attempt to define the fundamental genetic profile of its unique NK phenotypes. aCGH revealed hemizygous deletion of 6p containing genes responsible for hematopoietic functions. The SKY demonstrated that a constitutive reciprocal translocation, rcpt(5;14)(p13.2;q11) is a stable marker. Using somatic hybrids containing der(5) derived from SRIK-NKL, we found that the breakpoint in one homologue of no. 5 is located upstream of IL7R and also that the breakpoint in no. 14 is located within TRA@. The FISH analysis using a BAC which contains TRA@ and its flanking region further revealed a approximately 231kb deletion within 14q11 in the der(5) but not in the normal homologue of no. 14. The RT-PCR analysis detected mRNA for TRA@ transcripts which were extending across, but not including, the deleted region. IL7R was detected at least at mRNA levels. These findings were consistent with the immunological findings that TRA@ and IL7R are both expressed at mRNA levels and TRA@ at cytoplasmic protein levels in SRIK-NKL cells. In addition to rcpt(5;14), aCGH identified novel copy number abnormalities suggesting that the unique phenotype of the SRIK-NKL cell line is not solely due to the TRA@ rearrangement. These findings provide supportive evidence for the notion that SRIK-NKL cells may be useful for studying not only the function of NK cells but also genetic deregulations associated with leukemiogenesis.
Figures


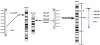
References
-
- Jonges LE, Albertson P, VanVlierberghe RLP, Ensink NG, Johanson BR, VanDevelde CJH, et al. The phenotypic heterogeneity of human natural killer cells: Presence of at least 48 different subsets in the peripheral blood. Scand J. Immunol. 2001;53:103–10. - PubMed
-
- Greer JP, Kinney MC, Loughran TP., Jr. B-cell and NK cell lymphoproliferative disorders. Hematology. Am. Soc. Hematology Euro. Program. 2003;1001:259–81. - PubMed
-
- Sivori S, Cantoni C, Prolini S, Marcenaro E, Conte R, Moretta L, et al. IL-21 induces both rapid maturation of human CD34+ cell precursors towards NK cells and acquisition of surface killer Ig-like receptors. Euro. J. Immunol. 2003;33:3439–47. - PubMed
-
- Drexler HG. Guide to Leukemia-Lymphoma Cell Lines. Braunschweig: 2005. For a CD with PDF file, please write to Dr. Drexler HG, is hdr@dsmz.de.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

