Protection against beta-amyloid induced abnormal synaptic function and cell death by Ginkgolide J
- PMID: 17640772
- PMCID: PMC2646106
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.05.025
Protection against beta-amyloid induced abnormal synaptic function and cell death by Ginkgolide J
Abstract
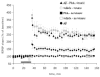
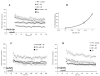
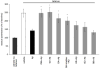
A new Ginkgo biloba extract P8A (TTL), 70% enriched with terpene trilactones, prevents A beta(1-42) induced inhibition of long-term potentiation in the CA1 region of mouse hippocampal slices. This neuroprotective effect is attributed in large part to ginkgolide J that completely replicates the effect of the extract. Ginkgolide J is also capable of inhibiting cell death of rodent hippocampal neurons caused by A beta(1-42). This beneficial and multi-faceted mode of action of the ginkgolide makes it a new and promising lead in designing therapies against Alzheimer's disease.
Figures
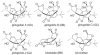
References
-
- Aksenov M, Aksenova M, Butterfield DA, Markesbery WR. Oxidative modification of creatine kinase BB in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Journal of neurochemistry. 2000;74(6):2520–7. - PubMed
-
- Andrieu S, Gillette S, Amouyal K, Nourhashemi F, Reynish E, Ousset PJ, Albarede JL, Vellas B, Grandjean H. Association of Alzheimer’s disease onset with ginkgo biloba and other symptomatic cognitive treatments in a population of women aged 75 years and older from the EPIDOS study. The journals of gerontology. 2003;58(4):372–7. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett H, Eperjesi F. An ideal ocular nutritional supplement? Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2004;24(4):339–49. - PubMed
-
- Bastianetto S, Zheng WH, Quirion R. The Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects and rescues hippocampal cells against nitric oxide-induced toxicity: involvement of its flavonoid constituents and protein kinase C. Journal of neurochemistry. 2000;74(6):2268–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

