Quantitative analyses reveal the importance of regulated Hdmx degradation for p53 activation
- PMID: 17640893
- PMCID: PMC1941475
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0701497104
Quantitative analyses reveal the importance of regulated Hdmx degradation for p53 activation
Abstract
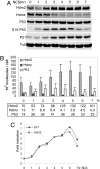
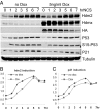
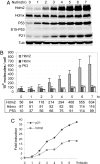
P53 regulates numerous downstream targets to induce cell cycle arrest, senescence, apoptosis, and DNA repair in response to diverse stresses. Hdm2 and Hdmx are critical negative regulators of P53 because Hdm2 regulates P53 abundance, and both can antagonize P53 transactivation. Modest changes in Hdm2 or Hdmx abundance affect P53 regulation, yet quantitative information regarding their endogenous intracellular concentrations and subcellular distributions during a stress response are lacking. We analyzed these parameters in normal and cancer cells after DNA damage. Our data show that the nuclear abundance of Hdm2 and Hdmx relative to P53 limits P53 activity in cells growing in culture. Upon DNA damage, P53 nuclear abundance increases, whereas Hdm2 and Hdmx stability decreases, which greatly limits their ability to antagonize P53, regardless of their levels. These data indicate that the damage-activated switch in Hdm2 ubiquitin ligase preference from P53 to itself and Hdmx is central to P53 activation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wahl GM, Stommel JM, Krummel KA, Wade M. In: 25 Years of p53 Research. Wiman K, Hainaut P, editors. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer; 2005. pp. 73–113.
-
- Jones SN, Roe AE, Donehower LA, Bradley A. Nature. 1995;378:206–208. - PubMed
-
- Montes de Oca Luna R, Wagner DS, Lozano G. Nature. 1995;378:203–206. - PubMed
-
- Parant J, Chavez-Reyes A, Little NA, Yan W, Reinke V, Jochemsen AG, Lozano G. Nat Genet. 2001;29:92–95. - PubMed
-
- Marine J-C, Francoz S, Maetens M, Wahl G, Toledo F, Lozano G. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:927–934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

