Mechanical and neural contributions to hysteresis in the cardiac vagal limb of the arterial baroreflex
- PMID: 17640929
- PMCID: PMC2277195
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.139204
Mechanical and neural contributions to hysteresis in the cardiac vagal limb of the arterial baroreflex
Abstract
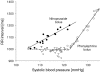
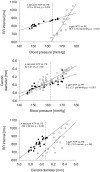
According to conventional wisdom, hysteresis in cardiac vagal baroreflex function exhibits a specific pattern: pressure falls are associated with longer heart periods and a smaller linear gain. A similar pattern occurs in the pressure-diameter relationship of barosensory vessels, and therefore it has been suggested that baroreflex hysteresis derives solely from vascular behaviour. However, we hypothesized that mechanical and neural baroreflex components contribute equally to baroreflex hysteresis. Blood pressure, carotid diameter and the electrocardiogram were recorded continuously during two trials of sequential bolus injections of nitroprusside and phenylephrine in 14 young healthy subjects. Baroreflex gain and its mechanical and neural components were estimated for falls and rises in pressure and diameter. The position or set point of the relations was quantified at the mean pressure and mean diameter. Gains were determined via piecewise linear regression. Set points and gains for falls versus rises in pressure and diameter were compared with the Chow test. Hysteresis was observed in all individuals, but not in every trial. In most, but not all, trials pressure falls were associated with longer heart periods and smaller linear gain, as conventional wisdom would predict. However, the pattern of hysteresis derived from the interaction of both mechanical and neural components. The two components most often acted in opposition to determine differences in set point, but in conjunction to determine differences in baroreflex gain. Therefore, we conclude that hysteresis is not solely determined by barosensory vessel behaviour but by the complex interaction of mechanical and neural aspects of the arterial baroreflex.
Figures

Comment in
-
The ups and downs of assessing baroreflex function.J Physiol. 2008 Mar 1;586(5):1209-11. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.149484. Epub 2008 Jan 10. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18187468 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Human sympathetic and vagal baroreflex responses to sequential nitroprusside and phenylephrine.Am J Physiol. 1999 May;276(5 Pt 2):H1691-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1999.276.5.h1691. Am J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10330255
-
Relating drug-induced changes in carotid artery mechanics to cardiovagal and sympathetic baroreflex control.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2005 May;83(5):439-46. doi: 10.1139/y05-030. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15897926
-
Quantification of mechanical and neural components of vagal baroreflex in humans.Hypertension. 2001 Jun;37(6):1362-8. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.37.6.1362. Hypertension. 2001. PMID: 11408378
-
Assessment of human baroreflex function using carotid ultrasonography: what have we learnt?Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2014 Jun;211(2):297-313. doi: 10.1111/apha.12302. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2014. PMID: 24739079 Review.
-
Barosensory vessel mechanics and the vascular sympathetic baroreflex: Impact on blood pressure homeostasis.Exp Physiol. 2023 Oct;108(10):1245-1249. doi: 10.1113/EP089686. Epub 2023 Apr 9. Exp Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37031381 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of ageing on carotid baroreflex peak response latency in humans.J Physiol. 2009 Nov 15;587(Pt 22):5427-39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.177998. Epub 2009 Oct 5. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19805748 Free PMC article.
-
Supine Parasympathetic Withdrawal and Upright Sympathetic Activation Underly Abnormalities of the Baroreflex in Postural Tachycardia Syndrome: Effects of Pyridostigmine and Digoxin.Hypertension. 2021 Apr;77(4):1234-1244. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.16113. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Hypertension. 2021. PMID: 33423527 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovagal Baroreflex Hysteresis Using Ellipses in Response to Postural Changes.Front Neurosci. 2021 Dec 9;15:720031. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.720031. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34955708 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Asymmetry of the Cardiac and Sympathetic Arms of the Baroreflex From Spontaneous Variability During Incremental Head-Up Tilt.Front Physiol. 2019 Apr 2;10:342. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00342. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31001137 Free PMC article.
-
The arterial baroreflex resets with orthostasis.Front Physiol. 2012 Dec 7;3:461. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00461. eCollection 2012. Front Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23233840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akaike H. Fitting autoregressive models for prediction. Ann I Stat Math. 1969;21:243–247.
-
- Bonyhay I, Jokkel G, Karlocai K, Reneman R, Kollai M. Effect of vasoactive drugs on carotid diameter in humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 1997;273:H1629–H1636. - PubMed
-
- Casadei B, Paterson DJ. Should we still use nitrovasodilators to test baroreflex sensitivity? J Hypertens. 2000;18:3–6. - PubMed
-
- Chapleau MW, Abboud FM. Contrasting effects of static and pulsatile pressure on carotid baroreceptor activity in dogs. Circ Res. 1987;61:648–658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

