Exercise hyperaemia: is anything obligatory but the hyperaemia?
- PMID: 17640934
- PMCID: PMC2277201
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.135889
Exercise hyperaemia: is anything obligatory but the hyperaemia?
Abstract
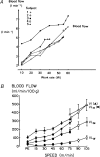
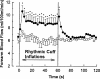
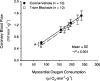
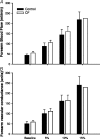
Exercise can increase skeletal muscle blood flow by 100-fold over values observed at rest. As this value was 3 to 4 times higher than so-called 'textbook' values at the time it raised a number of issues about cardiovascular control. However, there is a continuing inability to identify the factor or combination of factors that explain this substantial increase in muscle blood flow. Moreover, these governing mechanism(s) must also explain the precise matching of muscle blood flow to metabolic demand and oxygen use or need. The difficulties identifying the mechanisms for exercise hyperaemia are especially disappointing due to the essentially concurrent discovery in the 1980s that the vascular endothelium was a key site of vasomotor control and that nitric oxide (NO) potentially released from nerves, endothelial cells, directly from tissues such as skeletal muscle, or perhaps released from red blood cells, might participate in vascular control in a way that would permit blood flow and metabolism to be closely matched.
Figures

References
-
- Armstrong RB, Laughlin MH. Rat muscle blood flows during high-speed locomotion. J Appl Physiol. 1985;59:1322–1328. - PubMed
-
- Duncker DJ, Oei HH, Hu F, Stubenitsky R, Verdouw PD. Role of KATP+ channels in regulation of systemic, pulmonary, and coronary vasomotor tone in exercising swine. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001;280:H22–H33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

