Pemphigus IgG causes skin splitting in the presence of both desmoglein 1 and desmoglein 3
- PMID: 17640963
- PMCID: PMC1959479
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070028
Pemphigus IgG causes skin splitting in the presence of both desmoglein 1 and desmoglein 3
Abstract
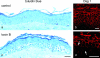
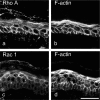
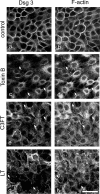
According to the desmoglein (Dsg) compensation concept, different epidermal cleavage planes observed in pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus have been proposed to be caused by different autoantibody profiles against the desmosomal proteins Dsg 1 and Dsg 3. According to this model, Dsg 1 autoantibodies would only lead to epidermal splitting in those epidermal layers in which no Dsg 3 is present to compensate for the functional loss of Dsg 1. We provide evidence that both pemphigus foliaceus-IgG containing Dsg 1- but not Dsg 3-specific antibodies and pemphigus vulgaris-IgG with antibodies to Dsg 1 and Dsg 3 were equally effective in causing epidermal splitting in human skin and keratinocyte dissociation in vitro. These effects were present where keratinocytes expressed both Dsg 1 and Dsg 3, demonstrating that Dsg 3 does not compensate for Dsg 1 inactivation. Rather, the cleavage plane in intact human skin caused by pemphigus autoantibodies was similar to the plane of keratinocyte dissociation in response to toxin B-mediated inactivation of Rho GTPases. Because we recently demonstrated that pemphigus-IgG causes epidermal splitting by inhibition of Rho A, we propose that Rho GTPase inactivation contributes to the mechanisms accounting for the cleavage plane in pemphigus skin splitting.
Figures
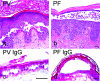
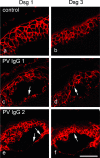
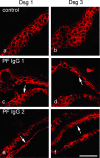
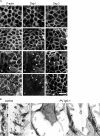
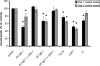
References
-
- Amagai M. Desmoglein as a target in autoimmunity and infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:244–252. - PubMed
-
- Amagai M, Ahmed AR, Kitajima Y, Bystryn JC, Milner Y, Gniadecki R, Hertl M, Pincelli C, Fridkis-Hareli M, Aoyama Y, Frusic-Zlotkin M, Muller E, David M, Mimouni D, Vind-Kezunovic D, Michel B, Mahoney M, Grando S. Are desmoglein autoantibodies essential for the immunopathogenesis of pemphigus vulgaris, or just “witnesses of disease”? Exp Dermatol. 2006;15:815. - PubMed
-
- Payne AS, Hanakawa Y, Amagai M, Stanley JR. Desmosomes and disease: pemphigus and bullous impetigo. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:536–543. - PubMed
-
- Stanley JR, Amagai M. Pemphigus, bullous impetigo, and the staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1800–1810. - PubMed
-
- Grando SA. Cholinergic control of epidermal cohesion. Exp Dermatol. 2006;15:265–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

