Pulmonary hypertension can be a sequela of prior Pneumocystis pneumonia
- PMID: 17640969
- PMCID: PMC1959506
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070178
Pulmonary hypertension can be a sequela of prior Pneumocystis pneumonia
Abstract
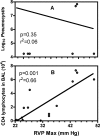
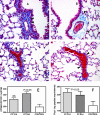
Improved treatment regimens have reduced fatalities from opportunistic diseases, such as Pneumocystis pneumonia, in AIDS patients. However, serious chronic conditions, including pulmonary hypertension (PH), are increasing in this group. We report here that when CD4 T cells in Pneumocystis-infected mice are temporally depleted and then allowed to return, the extended inflammation results in PH that persists after Pneumocystis is eliminated. Using this model of PH, we have found that i) the onset of PH is correlated with the return of CD4 T cells, but PH persists after CD4 levels diminish; ii) vascular remodeling accompanies PH, but whereas temporary medial hypertrophy is evident with transient PH in immunocompetent mice, persistent PH is associated with perivascular fibrosis; iii) elevated levels of the fibrotic mediator FIZZ1 are found in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of mice with persistent PH; and iv) although Th2-related mechanisms may be involved in PH etiology, PH still occurs in interleukin-4 receptor-deficient mice under these conditions. Overall, the data presented here demonstrate that the immune response to an infectious disease pathogen, such as Pneumocystis, can, when perturbed and prolonged, lead to later development of a serious chronic condition such as PH.
Figures


References
-
- Shelburne SA, III, Hamill RJ. The immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. AIDS Rev. 2003;5:67–79. - PubMed
-
- Stoll M, Schmidt RE. Adverse events of desirable gain in immunocompetence: the immune restoration inflammatory syndromes. Autoimmun Rev. 2004;3:243–249. - PubMed
-
- Rerkpattanapipat P, Wongpraparut N, Jacobs LE, Kotler MN. Cardiac manifestations of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:602–608. - PubMed
-
- Kanmogne GD. Noninfectious pulmonary complications of HIV/AIDS. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2005;11:208–212. - PubMed
-
- Kim KK, Factor SM. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis and plexogenic pulmonary arteriopathy in a homosexual man with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1987;18:1293–1296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

