The temporal dynamics model of emotional memory processing: a synthesis on the neurobiological basis of stress-induced amnesia, flashbulb and traumatic memories, and the Yerkes-Dodson law
- PMID: 17641736
- PMCID: PMC1906714
- DOI: 10.1155/2007/60803
The temporal dynamics model of emotional memory processing: a synthesis on the neurobiological basis of stress-induced amnesia, flashbulb and traumatic memories, and the Yerkes-Dodson law
Abstract
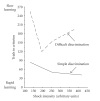
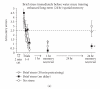
We have reviewed research on the effects of stress on LTP in the hippocampus, amygdala and prefrontal cortex (PFC) and present new findings which provide insight into how the attention and memory-related functions of these structures are influenced by strong emotionality. We have incorporated the stress-LTP findings into our "temporal dynamics" model, which provides a framework for understanding the neurobiological basis of flashbulb and traumatic memories, as well as stress-induced amnesia. An important feature of the model is the idea that endogenous mechanisms of plasticity in the hippocampus and amygdala are rapidly activated for a relatively short period of time by a strong emotional learning experience. Following this activational period, both structures undergo a state in which the induction of new plasticity is suppressed, which facilitates the memory consolidation process. We further propose that with the onset of strong emotionality, the hippocampus rapidly shifts from a "configural/cognitive map" mode to a "flashbulb memory" mode, which underlies the long-lasting, but fragmented, nature of traumatic memories. Finally, we have speculated on the significance of stress-LTP interactions in the context of the Yerkes-Dodson Law, a well-cited, but misunderstood, century-old principle which states that the relationship between arousal and behavioral performance can be linear or curvilinear, depending on the difficulty of the task.
Figures
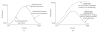


Similar articles
-
Competitive interactions between endogenous LTD and LTP in the hippocampus underlie the storage of emotional memories and stress-induced amnesia.Hippocampus. 2005;15(8):1006-25. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20107. Hippocampus. 2005. PMID: 16086429 Review.
-
Stress generates emotional memories and retrograde amnesia by inducing an endogenous form of hippocampal LTP.Hippocampus. 2004;14(3):281-91. doi: 10.1002/hipo.10186. Hippocampus. 2004. PMID: 15132427 Review.
-
Differential remoteness and emotional tone modulate the neural correlates of autobiographical memory.Brain. 2003 Mar;126(Pt 3):650-68. doi: 10.1093/brain/awg064. Brain. 2003. PMID: 12566286
-
Are the neural substrates of memory the final common pathway in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)?J Affect Disord. 2002 Jun;70(1):1-17. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0327(01)00351-2. J Affect Disord. 2002. PMID: 12113915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emotional and cognitive information processing: relations to behavioral performance and hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo during a spatial water maze training in rats.Learn Mem. 2010 Oct 26;17(11):552-60. doi: 10.1101/lm.1855610. Print 2010 Nov. Learn Mem. 2010. PMID: 20978118
Cited by
-
Cycloheximide impairs and enhances memory depending on dose and footshock intensity.Behav Brain Res. 2012 Aug 1;233(2):293-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2012.05.010. Epub 2012 May 17. Behav Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22610049 Free PMC article.
-
Tinnitus and Traumatic Memory.Brain Sci. 2022 Nov 20;12(11):1585. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12111585. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 36421908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative Emotional Arousal Impairs Associative Memory Performance for Emotionally Neutral Content in Healthy Participants.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 17;10(7):e0132405. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132405. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26186001 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between anxiety, centromedial amygdala volume, and complex verbal fluency in middle-aged to older adults.J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2022 Dec;44(10):730-742. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2023.2173149. Epub 2023 Feb 22. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2022. PMID: 36888757 Free PMC article.
-
Stress switches cannabinoid type-1 (CB1) receptor-dependent plasticity from LTD to LTP in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis.J Neurosci. 2013 Dec 11;33(50):19657-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3175-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24336729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim JJ, Diamond DM. The stressed hippocampus, synaptic plasticity and lost memories. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2002;3(6):453–462. - PubMed
-
- Diamond DM, Park CR, Woodson JC. Stress generates emotional memories and retrograde amnesia by inducing an endogenous form of hippocampal LTP. Hippocampus. 2004;14(3):281–291. - PubMed
-
- Diamond DM, Park CR, Campbell AM, Woodson JC. Competitive interactions between endogenous LTD and LTP in the hippocampus underlie the storage of emotional memories and stress-induced amnesia. Hippocampus. 2005;15(8):1006–1025. - PubMed
-
- Kim JJ, Song EY, Kosten TA. Stress effects in the hippocampus: synaptic plasticity and memory. Stress. 2006;9(1):1–11. - PubMed
-
- Post RM, Weiss SRB, Li H, et al. Neural plasticity and emotional memory. Development and Psychopathology. 1998;10(4):829–855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

