Pontocerebellar hypoplasia type 2: a neuropathological update
- PMID: 17641900
- PMCID: PMC2039791
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-007-0263-0
Pontocerebellar hypoplasia type 2: a neuropathological update
Abstract
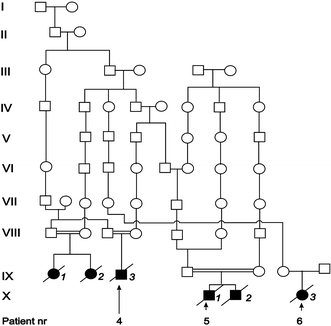
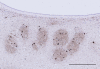
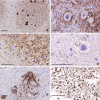
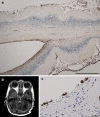
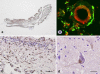
Pontocerebellar hypoplasia type 2 (PCH-2; MIM 277470), an autosomal recessive neurodegeneration with fetal onset, was studied in six autopsies with ages at death ranging between 1 and 22 years. Three patients were distantly related. A case of olivopontocerebellar hypoplasia (OPCH; MIM 225753) was studied for comparison. Typical findings are: short cerebellar folia with poor branching ("hypoplasia"), relative sparing of the vermis, sharply demarcated areas of full thickness loss of cerebellar cortex probably resulting from regression at an early stage of development, segmental loss of dentate nuclei with preserved islands and reactive changes, segmental loss in the inferior olivary nucleus with reactive changes, loss of ventral pontine nuclei with near absence of transverse pontine fibers and sparing of spinal anterior horn cells. Variable findings are: cystic cerebellar degeneration, found in two, with vascular changes limited to the cerebellum in one. Comparison to olivopontocerebellar hypoplasia (OPCH) strongly suggests a continuum of pathology between this disorder and PCH-2. Immunohistochemical evaluation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response is negative. We conclude that the neuropathological findings in PCH-2 are sufficiently specific to enable an unequivocal diagnosis based on neuropathology.
Figures
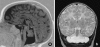
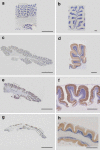

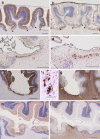


Comment in
-
Progress on pontocerebellar hypoplasia.Acta Neuropathol. 2007 Oct;114(4):401-2. doi: 10.1007/s00401-007-0282-x. Epub 2007 Aug 21. Acta Neuropathol. 2007. PMID: 17710422 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Arts WFM, Hofstee Y, Drejer GF, Beverstock GC, Oosterwijk JC (1995) Cerebellar and brainstem hypoplasia in a child with a partial monosomy for the short arm of chromosome 5 and partial trisomy for the short arm of chromosome 10. Neuropediatrics 26:41–44 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

