Influence of beta2-adrenoceptor gene polymorphisms on beta2-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in human lung mast cells
- PMID: 17643132
- PMCID: PMC2042952
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707400
Influence of beta2-adrenoceptor gene polymorphisms on beta2-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in human lung mast cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: Previous studies have shown that beta(2)-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in human lung mast cells are highly variable. The aims of the present study were to establish whether polymorphisms of the beta (2)-adrenoceptor gene (ADRB2) influence this variability in (a) beta(2)-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition and (b) desensitization of beta(2)-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in human lung mast cells.
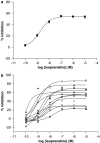
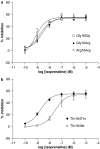
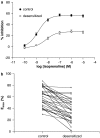
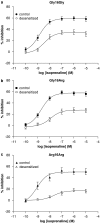
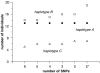
Experimental approach: Mast cells were isolated from human lung tissue. The inhibitory effects of the beta-adrenoceptor agonist, isoprenaline (10(-10)-10(-5) M), on IgE-mediated histamine release from mast cells were determined (n=92). Moreover, the inhibitory effects of isoprenaline were evaluated following a desensitizing treatment involving long-term (24 h) incubation of mast cells with isoprenaline (10(-6) M) (n=65). A potential influence of polymorphisms on these functional responses was determined by genotyping 11 positions, in the promoter and coding regions, of ADRB2 previously reported as polymorphic.
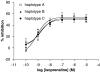
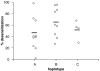
Key results: There was no influence of any of the polymorphic positions of ADRB2 on the potency of isoprenaline to inhibit histamine release from mast cells with the exception of position 491C>T (Thr164Ile). There was no influence of any of the polymorphic positions of ADRB2 on the extent of desensitization of the isoprenaline-mediated response following a desensitizing treatment except for position 46G>A (Gly16Arg). Analyses at the haplotype level indicated that there was no influence of haplotype on beta (2)-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in mast cells.
Conclusions and implications: These data indicate that certain polymorphisms in ADRB2 influence beta(2)-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in human lung mast cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Desensitisation of mast cell beta2-adrenoceptor-mediated responses by salmeterol and formoterol.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Jan;141(1):163-71. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705599. Epub 2003 Dec 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 14662724 Free PMC article.
-
Protection by dexamethasone of the functional desensitization to beta 2-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in human lung mast cells.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Jun;121(4):717-22. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701185. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9208139 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of receptor reserve on beta-adrenoceptor-mediated responses in human lung mast cells.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Jun;124(4):711-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701897. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9690863 Free PMC article.
-
Mast cell beta2-adrenoceptors.Chem Immunol Allergy. 2005;87:145-153. doi: 10.1159/000087641. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2005. PMID: 16107769 Review.
-
Beta-adrenoceptor responses of the airways: for better or worse?Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Mar 8;533(1-3):15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.12.060. Epub 2006 Feb 15. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16469310 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of in utero and childhood tobacco smoke exposure and beta2-adrenergic receptor genotype on childhood asthma and wheezing.Pediatrics. 2008 Jul;122(1):e107-14. doi: 10.1542/peds.2007-3370. Epub 2008 Jun 16. Pediatrics. 2008. PMID: 18558635 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated generation and analysis of N terminus polymorphic models of β2AR in isogenic hPSC-derived cardiomyocytes.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020 Oct 27;20:39-53. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2020.10.019. eCollection 2021 Mar 12. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020. PMID: 33335946 Free PMC article.
-
How "Neuronal" Are Human Skin Mast Cells?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 17;23(18):10871. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810871. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beta 2 Adrenergic Receptor Genetic Polymorphisms in Bronchial Asthma: Relationship to Disease Risk, Severity, and Treatment Response.Lung. 2018 Dec;196(6):673-680. doi: 10.1007/s00408-018-0153-3. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Lung. 2018. PMID: 30178312
-
Effects of the β-agonist, isoprenaline, on the down-regulation, functional responsiveness and trafficking of β2-adrenergic receptors with N-terminal polymorphisms.Cell Biol Int. 2012;36(12):1171-83. doi: 10.1042/CBI20120134. Cell Biol Int. 2012. PMID: 22938397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali H, Pearce FL. Isolation and properties of cardiac and other mast cells from the rat and guinea-pig. Agents Actions. 1985;16:138–140. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ. Effect of β2-agonists on inflammatory cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;104:S10–S17. - PubMed
-
- Brodde O-E, Leineweber K. β2-Adrenoceptor polymorphisms. Pharmacogenetics. 2005;15:267–275. - PubMed
-
- Büscher R, Eilmes KJ, Grasemann H, Torres B, Knauer N, Insel PA, et al. β2 Adrenoceptor gene polymorphisms in cystic fibrosis lung disease. Pharmacogenetics. 2002;12:347–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

