Toll-like receptor-4 signaling and Kupffer cells play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
- PMID: 17644211
- PMCID: PMC2094119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.04.019
Toll-like receptor-4 signaling and Kupffer cells play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Abstract
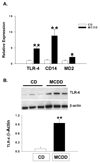
Background/aims: Studies in animal models and humans suggest a link between endotoxemia and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Since Kupffer cells are responsible for clearing endotoxin and are activated via endotoxin interaction with Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4), we examined the relationship between hepatic TLR-4 expression and Kupffer cell content during the genesis of steatohepatitis.
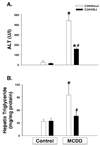
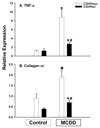
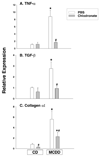
Methods: Male C57BL/6, C3H/HouJ and TLR-4 mutant C3H/HeJ mice were fed control or methionine/choline-deficient diet (MCDD). In one group of C57BL/6 mice, Kupffer cells were depleted by weekly intraperitoneal injections of clodronate liposomes. After 3 weeks, serum ALT activity and portal endotoxin levels were measured. Real-time PCR was used to examine mRNA expression of TLR-4, TLR-2, CD14, MD-2, TGFbeta, TNFalpha, CD36, PPAR-alpha, liver fatty acid binding protein (L-FABP) and collagen alpha1.
Results: We observed histological evidence typical of steatohepatitis, portal endotoxemia and enhanced TLR-4 expression in wild type mice fed MCDD. In contrast, injury and lipid accumulation markers were significantly lower in TLR-4 mutant mice. Destruction of Kupffer cells with clodronate liposomes blunted histological evidence of steatohepatitis and prevented increases in TLR-4 expression.
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate the importance of TLR-4 signaling and underscore a direct link between TLR-4 and Kupffer cells in the pathogenesis of steatohepatitis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor-2 deficiency enhances non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2010 May 28;10:52. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-52. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20509914 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in the development of fructose-induced hepatic steatosis in mice.Hepatology. 2009 Oct;50(4):1094-104. doi: 10.1002/hep.23122. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19637282
-
Caspase-1-mediated regulation of fibrogenesis in diet-induced steatohepatitis.Lab Invest. 2012 May;92(5):713-23. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2012.45. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Lab Invest. 2012. PMID: 22411067 Free PMC article.
-
Common pathogenic mechanism in development progression of liver injury caused by non-alcoholic or alcoholic steatohepatitis.J Toxicol Sci. 2007 Dec;32(5):453-68. doi: 10.2131/jts.32.453. J Toxicol Sci. 2007. PMID: 18198478 Review.
-
Kupffer cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the emerging view.J Hepatol. 2009 Jul;51(1):212-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.03.008. Epub 2009 Mar 31. J Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19447517 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiome and microbial metabolites in NAFLD and after bariatric surgery: Correlation and causality.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 20;13:1003755. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1003755. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36204626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of gut-liver axis in the pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2012 Dec;18(4):337-46. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2012.18.4.337. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 23323248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like receptors in liver fibrosis: cellular crosstalk and mechanisms.Front Physiol. 2012 May 22;3:138. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00138. eCollection 2012. Front Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22661952 Free PMC article.
-
The Gut-Liver Axis in Chronic Liver Disease: A Macrophage Perspective.Cells. 2021 Oct 30;10(11):2959. doi: 10.3390/cells10112959. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiome and metabolic diseases.Semin Immunopathol. 2014 Jan;36(1):103-14. doi: 10.1007/s00281-013-0399-z. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Semin Immunopathol. 2014. PMID: 24196453 Review.
References
-
- Yang S, Lin H, Diehl AM. Fatty liver vulnerability to endotoxin-induced damage despite NF-kappaB induction and inhibited caspase 3 activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001 Aug;281(2):G382–G392. - PubMed
-
- Li Z, Yang S, Lin H, Huang J, Watkins PA, Moser AB, et al. Probiotics and antibodies to TNF inhibit inflammatory activity and improve nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. 2003 Feb;37(2):343–350. - PubMed
-
- Vanderhoof JA, Metz MJ, Tuma DJ, Antonson DL, Sorrell MF. Effect of improved absorption on development of jejunoileal bypass- induced liver dysfunction in rats. Dig Dis Sci. 1980 Aug;25(8):581–586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

