Celastrus aculeatus Merr. suppresses the induction and progression of autoimmune arthritis by modulating immune response to heat-shock protein 65
- PMID: 17645785
- PMCID: PMC2206370
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2268
Celastrus aculeatus Merr. suppresses the induction and progression of autoimmune arthritis by modulating immune response to heat-shock protein 65
Abstract
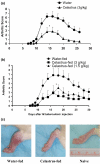
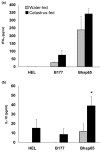
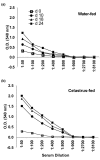
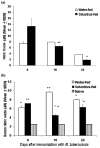
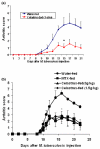
Complementary and alternative medicine products are increasingly being used for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. However, the mechanisms of action of these agents are not fully defined. Using the rat adjuvant arthritis (AA) model of human rheumatoid arthritis, we determined whether the ethanol extract of Celastrus aculeatus Merr. (Celastrus), a Chinese herb, can down-modulate the severity of AA, and also examined the Celastrus-induced changes in immune responses to the disease-related antigen mycobacterial heat-shock protein 65 (Bhsp65). AA was induced in the Lewis (LEW; RT.1l) rat by immunization subcutaneously with heat-killed M. tuberculosis H37Ra (Mtb). Celastrus was fed to LEW rats by gavage daily, beginning either before Mtb challenge (preventive regimen) or after the onset of AA (therapeutic regimen). An additional group of rats was given methotrexate for comparison. All rats were graded regularly for the signs of arthritis. In parallel, the draining lymph node cells of Celastrus-treated rats were tested for proliferative and cytokine responses, whereas their sera were tested for the inflammatory mediator nitric oxide. Celastrus feeding suppressed both the induction as well as the progression of AA, and the latter effect was comparable to that of methotrexate. Celastrus treatment induced relative deviation of the cytokine response to anti-inflammatory type and enhanced the production of anti-Bhsp65 antibodies, which are known to be protective against AA. Celastrus feeding also reduced the levels of nitric oxide. On the basis of our results, we suggest further systematic exploration of Celastrus as an adjunct therapeutic modality for rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T cells against the pathogenic and protective epitopes of heat-shock protein 65 are crossreactive and display functional similarity: novel aspect of regulation of autoimmune arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2007 Nov;34(11):2134-43. Epub 2007 Oct 15. J Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17937454
-
Green tea protects rats against autoimmune arthritis by modulating disease-related immune events.J Nutr. 2008 Nov;138(11):2111-6. doi: 10.3945/jn.108.089912. J Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18936206 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody responses to mycobacterial and self heat shock protein 65 in autoimmune arthritis: epitope specificity and implication in pathogenesis.J Immunol. 2006 Nov 15;177(10):6634-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.10.6634. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17082575
-
Diversification of response to hsp65 during the course of autoimmune arthritis is regulatory rather than pathogenic.Immunol Rev. 1998 Aug;164:175-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1998.tb01219.x. Immunol Rev. 1998. PMID: 9795775 Review.
-
Heat shock protein 60 and adjuvant arthritis: a model for T cell regulation in human arthritis.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2003 Aug;25(1):47-63. doi: 10.1007/s00281-003-0128-7. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2003. PMID: 12904891 Review.
Cited by
-
Complementary and alternative medicine use in rheumatoid arthritis: proposed mechanism of action and efficacy of commonly used modalities.Rheumatol Int. 2010 Mar;30(5):571-86. doi: 10.1007/s00296-009-1206-y. Epub 2009 Oct 30. Rheumatol Int. 2010. PMID: 19876631 Review.
-
Sinomenine suppresses osteoclast formation and Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra-induced bone loss by modulating RANKL signaling pathways.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 16;8(9):e74274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074274. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24066131 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-invasive effects of Celastrus Orbiculatus extract on interleukin-1 beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha combination-stimulated fibroblast-like synoviocytes.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Feb 19;14:62. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-62. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 24552146 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal cytokine expression and the target organ attributes unravel novel aspects of autoimmune arthritis.Indian J Med Res. 2013 Nov;138(5):717-31. Indian J Med Res. 2013. PMID: 24434324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Celastrus-derived celastrol suppresses autoimmune arthritis by modulating antigen-induced cellular and humoral effector responses.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 29;286(17):15138-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.226365. Epub 2011 Mar 14. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21402700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes PM, Powell-Griner E, McFann K, Nahin RL. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults: United States, 2002. Adv Data. 2004;343:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Taibi D, Bourguignon C. The role of complementary and alternative therapies in managing rheumatoid arthritis. Fam Community Health. 2003;26:41–52. - PubMed
-
- Zhang GG, Lee W, Bausell B, Lao L, Handwerger B, Berman B. Variability in the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) diagnoses and herbal prescriptions provided by three TCM practitioners for 40 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Altern Complement Med. 2005;11:415–421. doi: 10.1089/acm.2005.11.415. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

