Activation-coupled membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase membrane trafficking
- PMID: 17650075
- PMCID: PMC2049019
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070552
Activation-coupled membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase membrane trafficking
Abstract
The transmembrane collagenase MT1-MMP (membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase), also known as MMP-14, has a critical function both in normal development and in cancer progression, and is subject to extensive controls at the post-translational level which affect proteinase activity. As zymogen activation is crucial for MT1-MMP activity, an alpha1-PI (alpha1-proteinase inhibitor)-based inhibitor was designed by incorporating the MT1-MMP propeptide cleavage sequence into the alpha1-PI reactive-site loop (designated alpha1-PI(MT1)) and this was compared with wild-type alpha1-PI (alpha1-PI(WT)) and the furin inhibitory mutant alpha1-PI(PDX). Alpha1-PI(MT1) formed an SDS-stable complex with furin and inhibited proMT1-MMP activation. A consequence of the loss of MT1-MMP activity was the activation of proMMP-2 and the inhibition of MT1-MMP-mediated collagen invasion. alpha1-PI(MT1) expression also resulted in the intracellular accumulation of a glycosylated species of proMT1-MMP that was retained in the perinuclear region, leading to significantly decreased cell-surface accumulation of proMT1-MMP. These observations suggest that both the subcellular localization and the activity of MT1-MMP are regulated in a coordinated fashion, such that proMT1-MMP is retained intracellularly until activation of its zymogen, then proMT1-MMP traffics to the cell surface in order to cleave extracellular substrates.
Figures





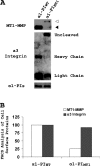
References
-
- Mayer G., Boileau G., Bendayan M. Furin interacts with proMT1-MMP and integrin αV at specialized domains of renal cell plasma membrane. J. Cell Sci. 2003;116:1763–1773. - PubMed
-
- Holmbeck K., Bianco P., Caterina J., Yamada S., Kromer M., Kuznetsov S. A., Mankani M., Robey P. G., Poole A. R., Pidoux I., et al. MT1-MMP-deficient mice develop dwarfism, osteopenia, arthritis, and connective tissue disease due to inadequate collagen turnover. Cell. 1999;99:81–92. - PubMed
-
- Hotary K. B., Allen E. D., Brooks P. C., Datta N. S., Long M. W., Weiss S. J. Membrane type I matrix metalloproteinase usurps tumor growth control imposed by the three-dimensional extracellular matrix. Cell. 2003;114:33–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

