Deafness alters auditory nerve fibre responses to cochlear implant stimulation
- PMID: 17650121
- PMCID: PMC2112941
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05678.x
Deafness alters auditory nerve fibre responses to cochlear implant stimulation
Abstract
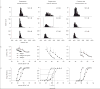
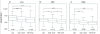
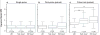
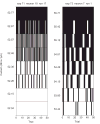
Here we characterized the relationship between duration of sensorineural hearing loss and the response of the auditory nerve to electrical stimulus rate. Electrophysiological recordings were made from undeafened guinea pigs and those ototoxically deafened for either 5 weeks or 6 months. Auditory neuron survival decreased significantly with the duration of deafness. Extracellular recordings were made from auditory nerve fibres responding to biphasic, charge-balanced current pulses delivered at rates of 20 and 200 pulses/s via a monopolar scala tympani stimulating electrode. The response to 20 pulses/s electrical stimulation of the deafened cochlea exhibited a decrease in spike latency, unaltered temporal jitter and unaltered dynamic range (of nerve firing rate against stimulus current), and a reduction in threshold after 6 months of deafness. The response to a 200-pulse/s stimulus was similar except that the dynamic range was greater than with 20 pulses/s and was also greater in deafened animals than in undeafened animals. Deafness and pulse rate are related; in deaf animals spike recovery appears to be complete between successive stimulus pulses at a low rate (20 pulses/s), but incomplete between pulses at a moderate pulse rate (200 pulses/s). These results suggest that changes in the function of individual auditory nerve fibres after deafness may affect clinical responses during high-rate stimulation such as that used in contemporary speech processing strategies, but not during lower rate stimulation such as that used to record evoked potentials.
Figures




References
-
- Black RC, Clark GM, O’Leary SJ, Walters C. Intracochlear electrical stimulation of normal and deaf cats investigated using brainstem response audiometry. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1983;399:5–17. - PubMed
-
- Blamey PJ, Ardnt P, Bergeron G, Brimacombe J, Facer G, Larky J, Lindstrom B, Nedzelski J, Peterson J, Peterson A, Shipp D, Staller S, Whitford L. Factors Affecting Auditory Performance of Postlinguistically Deaf Adults Using Cochlear Implants. Audiol Neurootol. 1996;1:293–306. - PubMed
-
- Bruce IC, Irlicht LS, White MW, O’Leary SJ, Javel E, Clark GM. A stochastic model of the electrically stimulated auditory nerve: single-pulse response. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1999;46:617–629. - PubMed
-
- Dodson HC, Mohuiddin A. Response of spiral ganglion neurones to cochlear hair cell destruction in the guinea pig. J Neurocytol. 2000;29:525–537. - PubMed
-
- Friedman L. Ph.D. Dissertation. University Of Melbourne; Australia: 2002. A retrospective study on the outcomes of cochlear implants in patients with otosclerosis.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

