PI3K activation is associated with intracellular sodium/iodide symporter protein expression in breast cancer
- PMID: 17651485
- PMCID: PMC1963336
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-137
PI3K activation is associated with intracellular sodium/iodide symporter protein expression in breast cancer
Abstract
Background: The sodium/iodide symporter (NIS) is a membrane glycoprotein mediating active iodide uptake in the thyroid gland and is the molecular basis for radioiodide imaging and therapeutic ablation of thyroid carcinomas. NIS is expressed in the lactating mammary gland and in many human breast tumors, raising interest in similar use for diagnosis and treatment. However, few human breast tumors have clinically evident iodide uptake ability. We previously identified PI3K signaling as important in NIS upregulation in transgenic mouse models of breast cancer, and the PI3K pathway is commonly activated in human breast cancer.
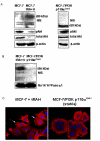
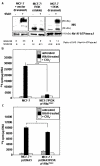
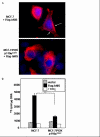
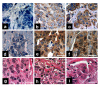
Methods: NIS expression, subcellular localization, and function were analyzed in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells and MCF-7 cells stably or transiently expressing PI3K p110alpha subunit using Western blot of whole cell lysate, cell surface biotinylation Western blot and immunofluorescence, and radioiodide uptake assay, respectively. NIS localization was determined in a human breast cancer tissue microarray using immunohistochemical staining (IHC) and was correlated with pre-existing pAkt IHC data. Statistical analysis consisted of Student's t-test (in vitro studies) or Fisher's Exact Test (in vivo correlational studies).
Results: In this study, we demonstrate that PI3K activation in MCF-7 human mammary carcinoma cells leads to expression of underglycosylated NIS lacking cell surface trafficking necessary for iodide uptake ability. PI3K activation also appears to interfere with cell surface trafficking of exogenous NIS as well as all-trans retinoic acid-induced endogenous NIS. A correlation between NIS expression and upregulation of PI3K signaling was found in a human breast cancer tissue microarray.
Conclusion: Thus, the PI3K pathway likely plays a major role in the discordance between NIS expression and iodide uptake in breast cancer patients. Further study is warranted to realize the application of NIS-mediated radioiodide ablation in breast cancer.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society, Breast Cancer http://www.cancer.org
-
- Taurog A. Hormone Synthesis. In: Braverman LL, Utiger RD, editor. Werner and Ingbar's The Thyroid: A Fundamental and Clinical Text. 7. Philadelphia, PA: J.B. Lippincott Co; 1996. pp. 47–81.
-
- Cotran RS, Kumar V, Collins T. The Endocrine System. In: Cotran RS, Kumar V, Collins T, editor. Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease. 6. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Company; 1999. pp. 1142–1147.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

