A recombinant Sendai virus is controlled by CD4+ effector T cells responding to a secreted human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein
- PMID: 17652379
- PMCID: PMC2168998
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00197-07
A recombinant Sendai virus is controlled by CD4+ effector T cells responding to a secreted human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein
Abstract
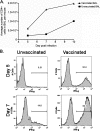
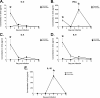
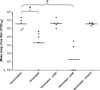
The importance of antigen-specific CD4(+) helper T cells in virus infections is well recognized, but their possible role as direct mediators of virus clearance is less well characterized. Here we describe a recombinant Sendai virus strategy for probing the effector role(s) of CD4(+) T cells. Mice were vaccinated with DNA and vaccinia virus recombinant vectors encoding a secreted human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope protein and then challenged with a Sendai virus carrying a homologous HIV-1 envelope gene. The primed mice showed (i) prompt homing of numerous envelope-primed CD4(+) T cell populations to the virus-infected lung, (ii) substantial production of gamma interferon, and interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-4, and IL-5 in that site, and (iii) significantly reduced pulmonary viral load. The challenge experiments were repeated with immunoglobulin(-/-) microMT mice in the presence or absence of CD8(+) and/or CD4(+) T cells. These selectively immunodeficient mice were protected by primed CD4(+) T cells in the absence of antibody or CD8(+) T cells. Together, these results highlight the role of CD4(+) T cells as direct effectors in vivo and, because this protocol gives such a potent response, identify an outstanding experimental model for further dissecting CD4(+) T-cell-mediated immunity in the lung.
Figures

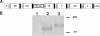


References
-
- Allan, W., Z. Tabi, A. Cleary, and P. C. Doherty. 1990. Cellular events in the lymph node and lung of mice with influenza. Consequences of depleting CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 144:3980-3986. - PubMed
-
- Belyakov, I. M., M. A. Derby, J. D. Ahlers, B. L. Kelsall, P. Earl, B. Moss, W. Strober, and J. A. Berzofsky. 1998. Mucosal immunization with HIV-1 peptide vaccine induces mucosal and systemic cytotoxic T lymphocytes and protective immunity in mice against intrarectal recombinant HIV-vaccinia challenge. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:1709-1714. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

