Expression and function of cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 and their cognate cannabinoid ligands in murine embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 17653268
- PMCID: PMC1919431
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000641
Expression and function of cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 and their cognate cannabinoid ligands in murine embryonic stem cells
Abstract
Background: Characterization of intrinsic and extrinsic factors regulating the self-renewal/division and differentiation of stem cells is crucial in determining embryonic stem (ES) cell fate. ES cells differentiate into multiple hematopoietic lineages during embryoid body (EB) formation in vitro, which provides an experimental platform to define the molecular mechanisms controlling germ layer fate determination and tissue formation.
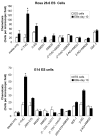
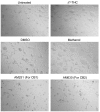
Methods and findings: The cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2) are members of the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) family, that are activated by endogenous ligands, the endocannabinoids. CB1 receptor expression is abundant in brain while CB2 receptors are mostly expressed in hematopoietic cells. However, the expression and the precise roles of CB1 and CB2 and their cognate ligands in ES cells are not known. We observed significant induction of CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors during the hematopoietic differentiation of murine ES (mES)-derived embryoid bodies. Furthermore, mES cells as well as ES-derived embryoid bodies at days 7 and 14, expressed endocannabinoids, the ligands for both CB1 and CB2. The CB1 and CB2 antagonists (AM251 and AM630, respectively) induced mES cell death, strongly suggesting that endocannabinoids are involved in the survival of mES cells. Treatment of mES cells with the exogenous cannabinoid ligand Delta(9)-THC resulted in the increased hematopoietic differentiation of mES cells, while addition of AM251 or AM630 blocked embryoid body formation derived from the mES cells. In addition, cannabinoid agonists induced the chemotaxis of ES-derived embryoid bodies, which was specifically inhibited by the CB1 and CB2 antagonists.
Conclusions: This work has not been addressed previously and yields new information on the function of cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2, as components of a novel pathway regulating murine ES cell differentiation. This study provides insights into cannabinoid system involvement in ES cell survival and hematopoietic differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
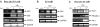

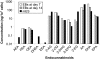
Similar articles
-
Reduction of human monocytic cell neurotoxicity and cytokine secretion by ligands of the cannabinoid-type CB2 receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Jun;139(4):775-86. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705304. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12813001 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of immunomodulatory effects of mouse bone-marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells by tetrahydrocannabinol pre-treatment involving cannabinoid receptor CB2.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 9;7(6):6436-47. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7042. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26824325 Free PMC article.
-
2-Arachidonoyl-glycerol suppresses interferon-gamma production in phorbol ester/ionomycin-activated mouse splenocytes independent of CB1 or CB2.J Leukoc Biol. 2005 Jun;77(6):966-74. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1104652. Epub 2005 Mar 17. J Leukoc Biol. 2005. PMID: 15774549
-
Cannabinoid receptor signaling in progenitor/stem cell proliferation and differentiation.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):633-50. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.05.004. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 24076098 Review.
-
The pharmacology of cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: an overview.Int J Obes (Lond). 2006 Apr;30 Suppl 1:S13-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0803272. Int J Obes (Lond). 2006. PMID: 16570099 Review.
Cited by
-
Cannabinoid Actions on Neural Stem Cells: Implications for Pathophysiology.Molecules. 2019 Apr 5;24(7):1350. doi: 10.3390/molecules24071350. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30959794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of endocannabinoid signalling on cell fate: life, death, differentiation and proliferation of brain cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 May;176(10):1361-1369. doi: 10.1111/bph.14369. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 29797438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling the Effect of Cannabinoid Exposure During Human Neurodevelopment Using Bidimensional and Tridimensional Cultures.Cells. 2025 Jan 7;14(2):70. doi: 10.3390/cells14020070. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39851498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contributions of endocannabinoid signaling to psychiatric disorders in humans: genetic and biochemical evidence.Neuroscience. 2012 Mar 1;204:207-29. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.11.020. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22123166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G protein coupled receptors in embryonic stem cells: a role for Gs-alpha signaling.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 8;5(2):e9105. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009105. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20161705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Downing GJ, Battey JF., Jr Technical assessment of the first 20 years of research using mouse embryonic stem cell lines. Stem Cells. 2004;22:1168–1180. - PubMed
-
- Matsuoka S, Tsuji K, Hisakawa H, Xu Mj, Ebihara Y, et al. Generation of definitive hematopoietic stems cells from murine early yolk sac and paraaortic splanchnopleures by aorta-gonad-mesonephros region-derived stromal cells. Blood. 2001;98:6–12. - PubMed
-
- Metcalf D. The unsolved enigmas of leukemia inhibitory factor. Stem Cells. 2003;21:5–14. - PubMed
-
- Viswanathan S, Benatar T, Rose-John S, Lauffenburger DA, Zandstra PW. Ligand/receptor signaling threshold (LIST) model accounts for gp130-mediated embryonic stem cell self-renewal responses to LIF and HIL-6. Stem Cells. 2002;20:119–138. - PubMed
-
- Nishikawa SI, Nishikawa S, Hirashima M, Matsuyoshi N, Kodama H. Progressive lineage analysis by cell sorting and culture identifies FLK1+VE-cadherin+ cells at a diverging point of endothelial and hemopoietic lineages. Development. 1998;125:1747–1757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

