Multiple active site histidine protonation states in Acetobacter aceti N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide mutase detected by REDOR NMR
- PMID: 17655332
- PMCID: PMC2793534
- DOI: 10.1021/bi700899q
Multiple active site histidine protonation states in Acetobacter aceti N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide mutase detected by REDOR NMR
Abstract
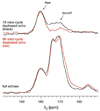
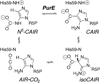
Class I PurE (N5-carboxyaminoimidazole mutase) catalyzes a chemically unique mutase reaction. A working mechanistic hypothesis involves a histidine (His45 in Escherichia coli PurE) functioning as a general acid, but no evidence for multiple protonation states has been obtained. Solution NMR is a peerless tool for this task but has had limited application to enzymes, most of which are larger than its effective molecular size limit. Solid-state NMR is not subject to this limit. REDOR NMR studies of a 151 kDa complex of uniformly 15N-labeled Acetobacter aceti PurE (AaPurE) and the active site ligand [6-13C]citrate probed a single ionization equilibrium associated with the key histidine (AaPurE His59). In the AaPurE complex, the citrate central carboxylate C6 13C peak moves upfield, indicating diminution of negative charge, and broadens, indicating heterogeneity. Histidine 15N chemical shifts indicate His59 exists in approximately equimolar amounts of an Ndelta-unprotonated (pyridine-like) form and an Ndelta-protonated (pyrrole-like) form, each of which is approximately 4 A from citrate C6. The spectroscopic data are consistent with proton transfers involving His59 Ndelta that are invoked in the class I PurE mechanism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Biochemical and structural studies of N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide mutase from the acidophilic bacterium Acetobacter aceti.Biochemistry. 2006 Jul 11;45(27):8193-208. doi: 10.1021/bi060465n. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16819818
-
Acidophilic adaptations in the structure of Acetobacter aceti N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide mutase (PurE).Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2004 Oct;60(Pt 10):1753-60. doi: 10.1107/S090744490401858X. Epub 2004 Sep 23. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2004. PMID: 15388921
-
N5-CAIR mutase: role of a CO2 binding site and substrate movement in catalysis.Biochemistry. 2007 Mar 13;46(10):2842-55. doi: 10.1021/bi602436g. Epub 2007 Feb 14. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17298082 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for the direct transfer of the carboxylate of N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide (N5-CAIR) to generate 4-carboxy-5-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide catalyzed by Escherichia coli PurE, an N5-CAIR mutase.Biochemistry. 1999 Mar 9;38(10):3012-8. doi: 10.1021/bi9827159. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10074353
-
The roles of Glu-327 and His-446 in the bisphosphatase reaction of rat liver 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase probed by NMR spectroscopic and mutational analyses of the enzyme in the transient phosphohistidine intermediate complex.Biochemistry. 1999 Apr 6;38(14):4471-9. doi: 10.1021/bi9828728. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10194369
Cited by
-
Structural and biochemical characterization of N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide synthetase and N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide mutase from Staphylococcus aureus.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2011 Aug;67(Pt 8):707-15. doi: 10.1107/S0907444911023821. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2011. PMID: 21795812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mueller EJ, Meyer E, Rudolph J, Davisson VJ, Stubbe J. N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide: evidence for a new intermediate and two new enzymatic activities in the de novo purine biosynthetic pathway of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1994;33:2269–2278. - PubMed
-
- Kappock TJ, Ealick SE, Stubbe J. Modular evolution of the purine biosynthetic pathway. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2000;4:567–572. - PubMed
-
- Meyer E, Kappock TJ, Osuji C, Stubbe J. Evidence for the direct transfer of the carboxylate of N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide (N5-CAIR) to generate 4-carboxy-5-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide catalyzed by Escherichia coli PurE, an N5-CAIR mutase. Biochemistry. 1999;38:3012–3018. - PubMed
-
- Firestine SM, Poon S-W, Mueller EJ, Stubbe J, Davisson VJ. Reactions catalyzed by 5-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide carboxylases from Escherichia coli and Gallus gallus: a case for divergent catalytic mechanisms. Biochemistry. 1994;33:11927–11934. - PubMed
-
- Mathews II, Kappock TJ, Stubbe J, Ealick SE. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli PurE, an unusual mutase in the purine biosynthetic pathway. Structure Fold. Des. 1999;7:1395–1406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

